The Hide – Shillim, India
Stretching like a mountainous spine down the western edge of India, the Western Ghats are a unique mountain range that harbours an incredible diversity of flora and fauna . Although most of the Western Ghats appear more like rolling hills than craggy snow-covered peaks, parts of it do reach over 2,000 metres and it contains the highest mountain in India, the Anaimudi, at 2,695 metres.
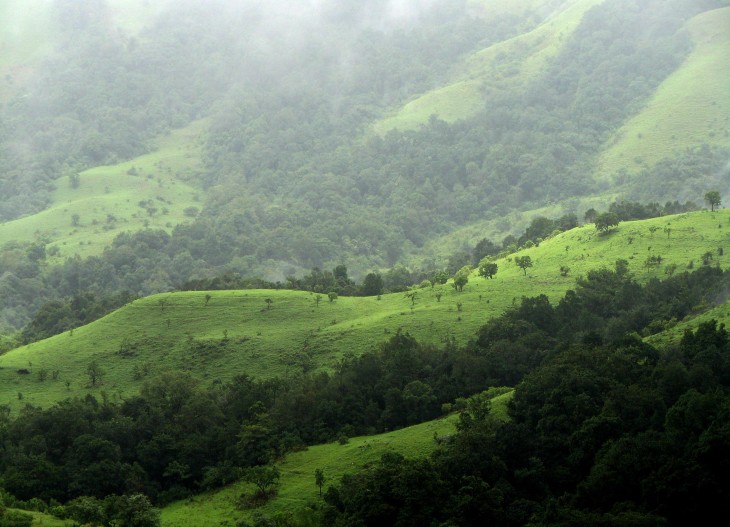

Older than the Himalaya mountains are the mountain chain of the Western Ghats representing the geomorphic features of immense importance with unique biophysical and ecological processes. The site’s high mountain forest ecosystems influence the Indian monsoon weather pattern. It also has an exceptionally high level of biological diversity and endemism and is recognized as one of the world’s eight hotspots of biological diversity. The forests of the site include some of the best representatives of non-equatorial tropical evergreen forests anywhere and are home to at least 325 globally threatened flora, fauna, bird, amphibian, reptile and fish species. The mountains of the Western Ghats are the second most important shelter in the world for threatened species, says a research paper edition of the international journal, Science.
The Shillim Foundation
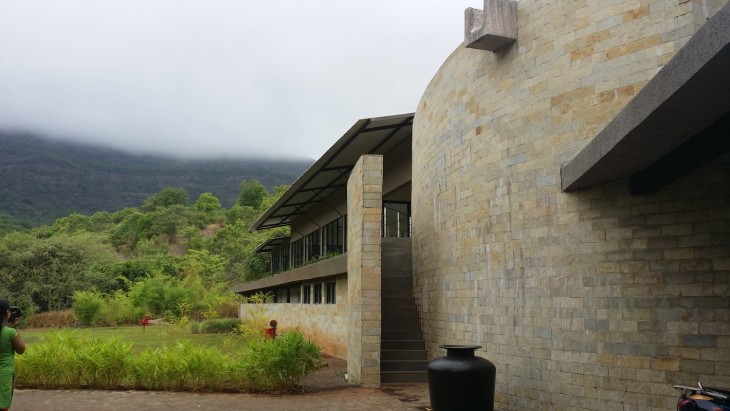

Shillim is a valley in the state of Maharashtra, about 3 hour drive from Pune. The valley is now being conserved or developed by the Shillim foundation by setting up a Shillim Institute. The Shillim Foundation is an international arm of the Shillim Institute, which is located at the heart of the Shillim Retreat in the Western Ghats. The mission of the Shillim Institute is to generate ideas and facilitate positive action in the areas of conservation, sustainability and healing.
Hilton shillim Estate Resort and Spa

The Shillim Valley is a part of the Western Ghats, one of the hottest hotspots of biodiversity in the word and known for its rich endemism. For a region that is a gift of nature, the Architecture has to be delicately treated and empathized. Clearly, the architecture of the Hilton Resort is wrong. The existing architecture does not belong to the place and is a misplace, considering the beauty of the region. Inspite of the openness of the buildings, it is the material and the construction process that hurts one to see such an architecture in a Valley, so filled with Mother Earth.
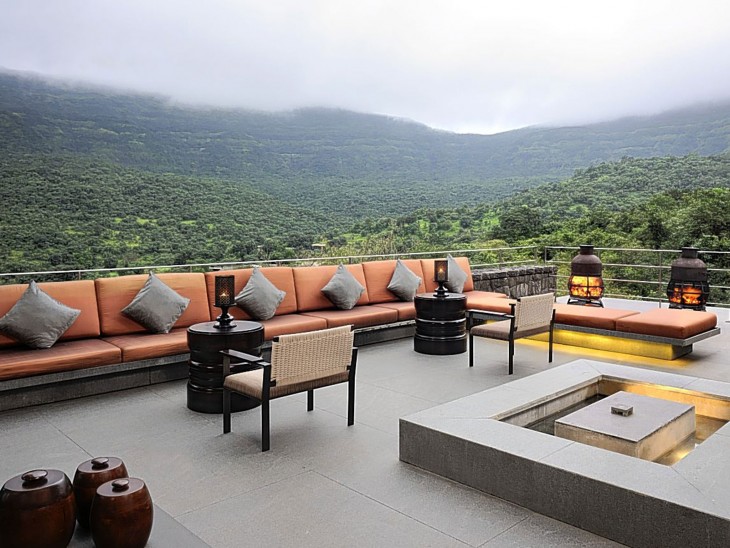

Tourism is another enemy of Nature. The tourists visit the resort as a getaway and expect the luxuries that they would not get at home during their routine. Keeping humans and not Nature at the centre of the design is the reason for the diminishing ecosystems and degradation of the biodiversity of the valley. The presence of this resort is increasing the pressure on the ecosystem and this in turn would adversely affect the already vulnerable species. Should this continue for a longer duration of time, the place would be completely engulfed by the human activities. In the coming years, the vulnerable species would soon be extinct and and the existence of these species will be a history. Thus, it is time we realise how much our luxury and tourism is going to cost us and replace this architecture with the one that would blend with Nature.
The Action Plans

Target: To raze down or deconstruct buildings or element that create imbalance in the bioreserve at Shillim. The structures built by the Hilton Hotel and Spa, we believe, are harmful to the ecosystem of the place. The carbon footprint of these structures clearly show that the architecture of these buildings are not sustainable with respect to the surrounding. Hilton is one of the most established chain of hotels and with celebrities and business class of people visiting Shillim as a get-away place, it will be quite a task for the activists to raze down this deep routed structure. Evolving from a concrete structure to a structure that would merge with nature is a process.

1. Building structures that are suitable to the place close to the existing resorts so the visitors empathise with nature. 2. The new structures should really grab the attention and be interactive. 3. The new low-footprint structures stand as a fight for each of the villas to be deconstructed. 4. The villas will not be raised down at one go but as a process of change. 5. The villas will not be demolished but deconstructed and be used in the new buildings or used for other purposes.
Preservation of Biodiversity
The Western Ghats supports a diverse fauna. Among the vertebrates, birds represent the largest number of known species (508 species), followed by fishes (218), reptiles (157), mammals (137), and amphibians (126). Many of these species are endemic to the Western Ghats region. The greatest number of endemics is found among the amphibians (78 percent) followed by reptiles (62 percent), fish (53 percent), mammals (12 percent), and birds (4 percent).
The remnant natural ecosystems of the Western Ghats are currently subject to a plethora of threats that vary widely in the nature and intensity of their impacts on biodiversity. Proximate threats fall into two broad categories: localized threats such as illegal hunting, livestock grazing, and forest fires, and landscape-level threats such as mining, roads, large and micro-hydel power projects, wind farms, large-scale agricultural expansion, and creation of monoculture plantations. All these threats either independently or synergistically influence biodiversity in the hotspot. Very often, threats are intricately meshed together in complex and myriad ways making it a difficult challenge to tease apart their impacts.
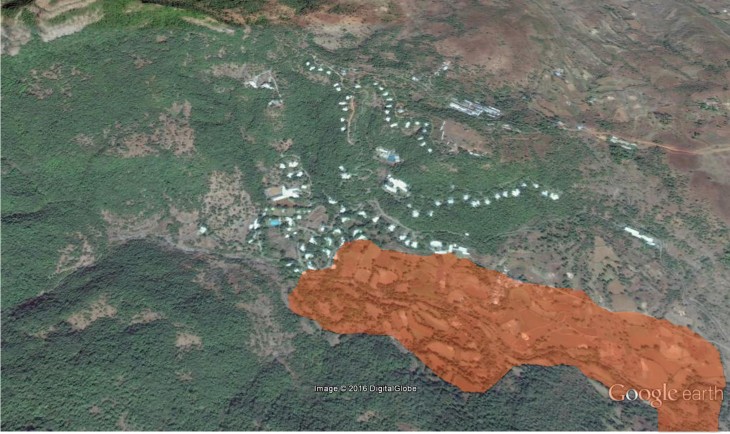
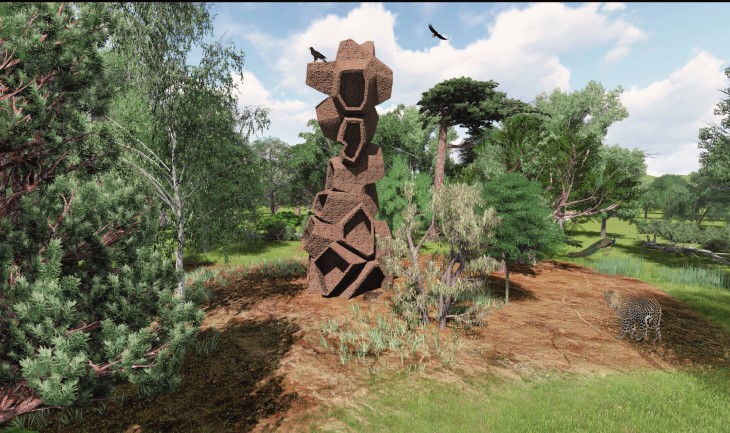
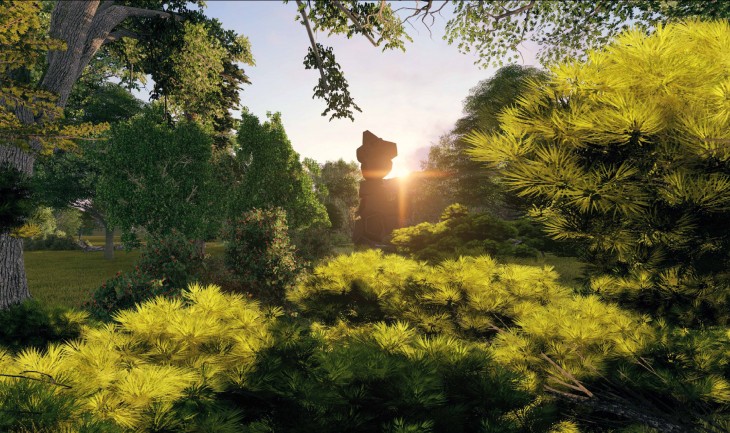
This zone in the campus will be declared as a Preservation zone. No human zone and entry will be permitted in the zone. It will be interesting to see how the zone increases over Time, thus increasing the count of the endangered species.
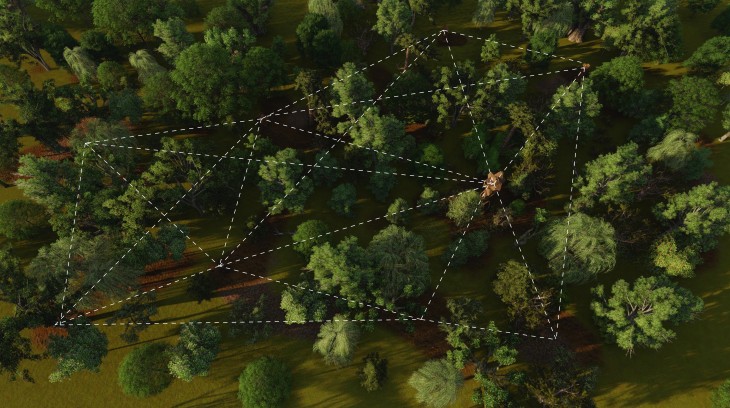
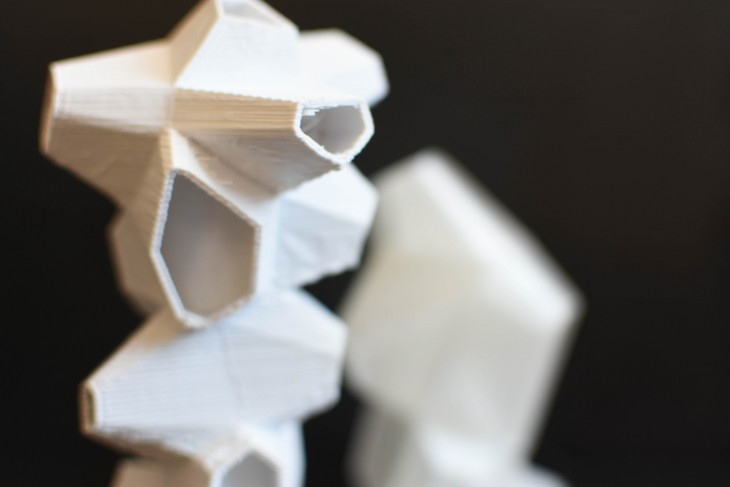
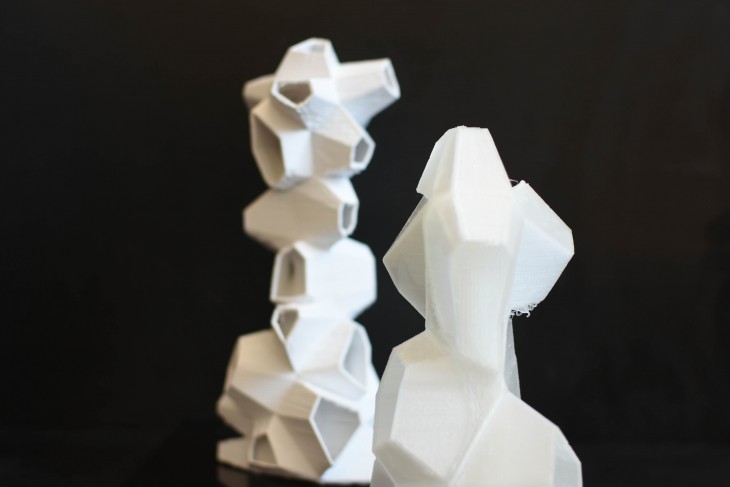
The Hides will be located amidst the trees in several locations. The size and shape of the hides depends on the surrounding trees and the ecosystems. These hides behave as nests, thus providing habitat for the animals and contributing to the biodiversity.
The Food Web
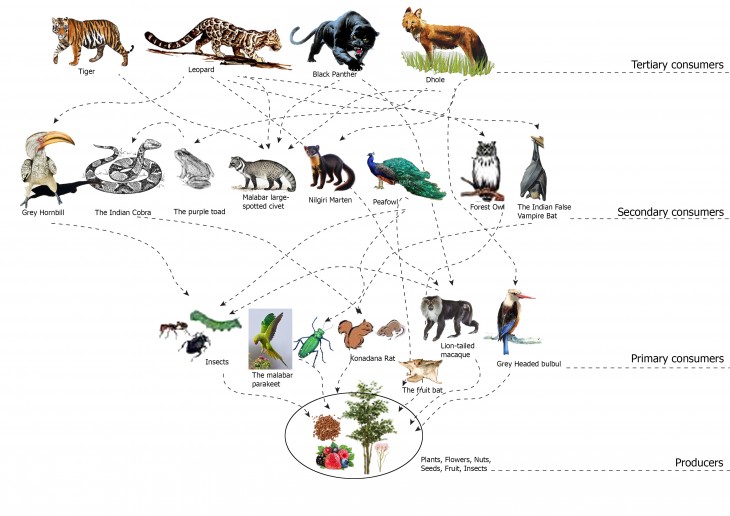
Food web is the living component of a biosphere. The transfer of energy and nutrients from one level of consumers to another level can be traced by understanding the food web. In case of traces of any chemical in the lower levels of the food web, these chemicals will accumulate exponentially, thus harming the carnivores or the scanvengers to a large extent. Veterinary use of the drug diclofenac—used in the treatment of livestock—has been linked to the collapse of vulture populations throughout South Asia. Vultures are keystone species that perform a vital ecosystem service by disposing of carrion and their decline has had dramatic ecological and socio-economic consequences. Understanding the food web also helps one manage the biodiversity. Some species tend to multiply rapidly, causing an imbalance in the ecosystem.
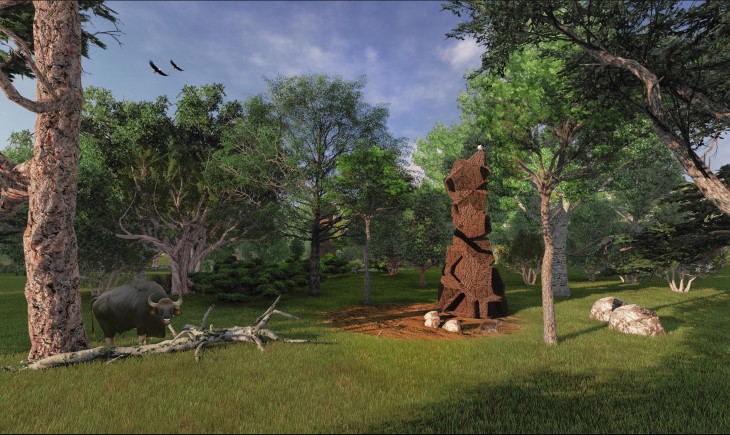

The building behaves as a hide for students/photographers to document the animals. The building also in turn regenerates the habitat once lost. This releases the pressure on the ecosystem and accelerates the increase in the numbers of the animals. Land fragmentation is also an important cause of decline in numbers. WIth the well-defined constitution, the land is declared as a no human-use zone. This ensures only anout 5-6 persons within the zone with special permits. The hide also enables observes to manage the preservaion process. It keeps check on the increasing or decreasing numbers of the animals and plant species. Many of the organisms have gone undocumented. The data serves as an open source for the others to have direct access to. The increase in the number of these hides would mean a rapidly growing animal population, which would mean a positive aspect for the Western Ghats.
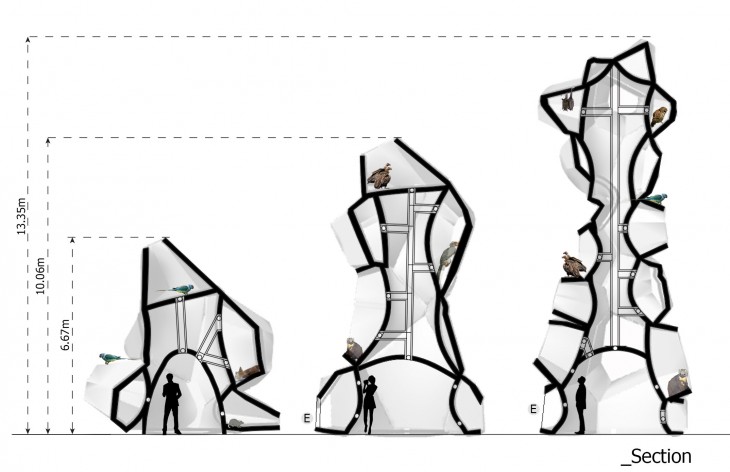
The height and size of the openings will depend based on the comfort level of the organism. By studying the endemic speices and their numbers and position in the food web, the heights and opening sizes can be generated. The animals and birds nesting in these openings will be a natural process, depending on the choices of the species.
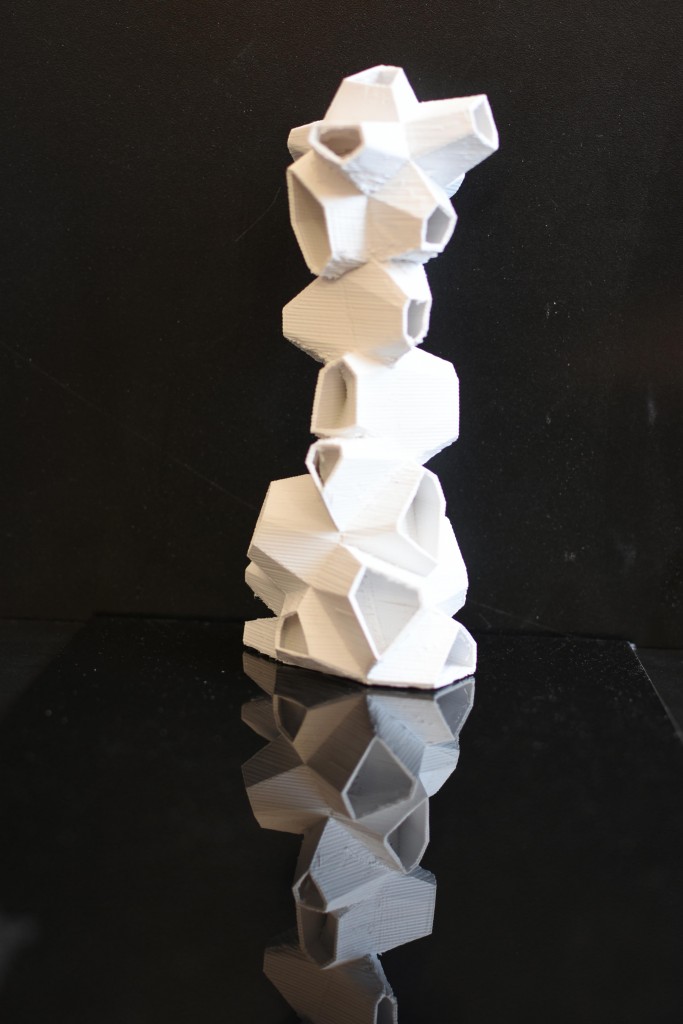

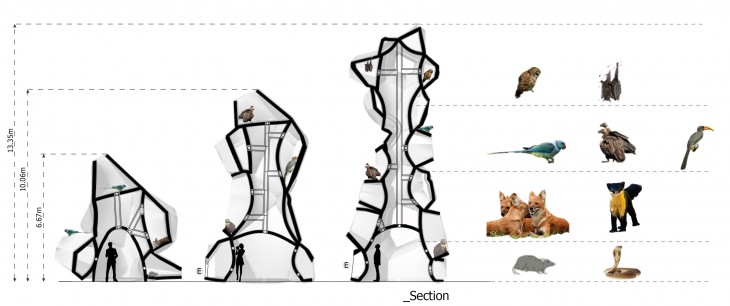
The buildings could vary in dimension depending on the class of animals it is accommodating and the space available. The animals live in at particular height and environment they are comfortable in. The height and size of the openings play an important role in the building.
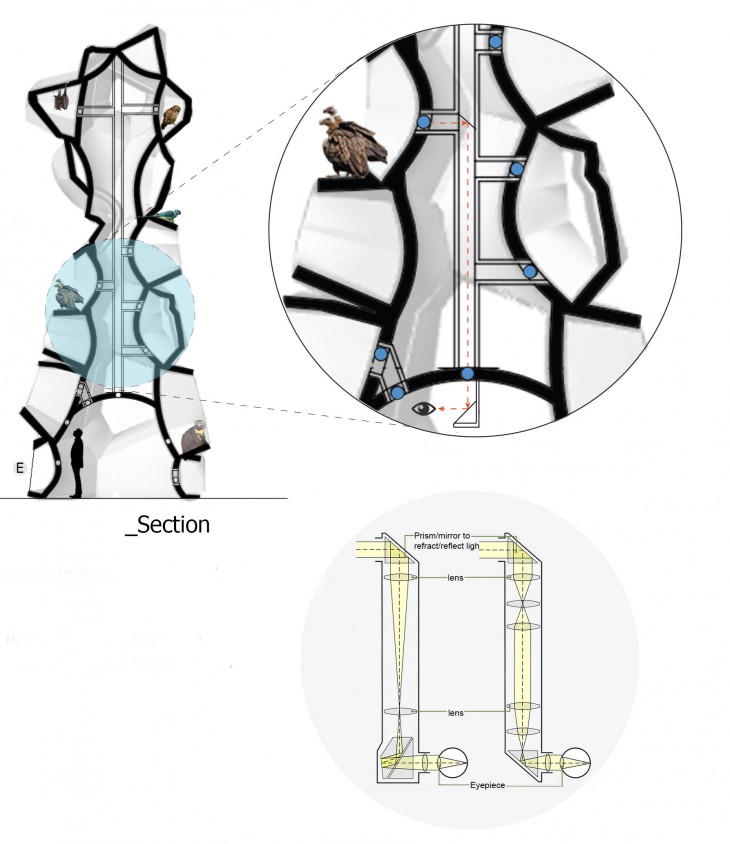
The building is a hide for the students/visitors (with special permission) to document the animals in the region. The building has a central optical tube behaving like a periscope. It enables the persons in the hide to zoom in or study the behaviour of the animals in their nest or outside the building. The building has a central optical tube behaving like a periscope. It enables the persons in the hide to zoom in or study the behaviour of the animals in their nest or outside the building.

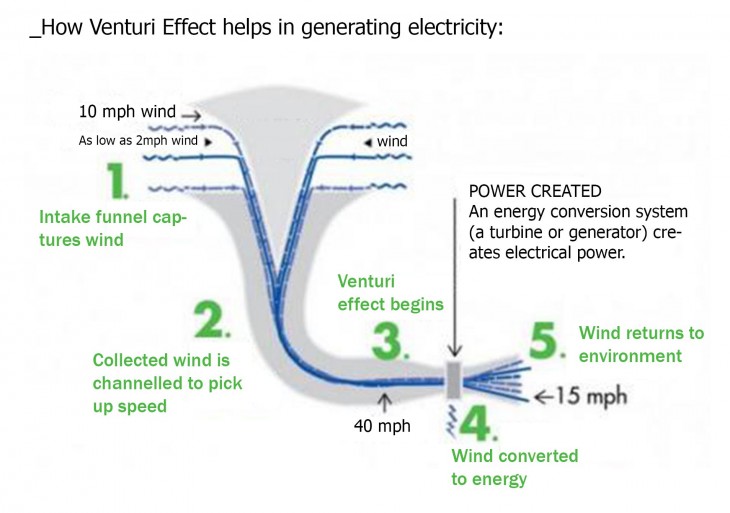
The Venturi effect is the phenomenonthat occurs when a fluid that is flowing through a pipe is forced through a narrow section, resulting in a pressure decrease and a velocity increase.
Multiple turbines can be used in a row or series increasing output exponentially depending on th usage.
This system will generate enough energy for the persons in the hide to charge their electronic devices and also ventilate the space.
An equationfor the drop in pressure due to the Venturi effect may bederived from a combination of Bernoulli’s principle andthe continuity equation.
P + ½mV2+ ?g h = constant
Where:A = area, V = velocity, ? = density of fluid, g = acceleration constant, h = height, P = fluid pressure.





The Hide is a project of IaaC, Institute for Advanced Architecture of Catalonia developed at Master in Advanced Architecture in 2015 – 2016 by:
Students: Varsha Subba Rao
Faculty: Enric Ruiz-Geli, Mireia Luzárraga