Tourism and its impacts on delicate ecosystems.
Let’s think about your last trip. What it was? New York, or maybe Mumbai? White sandy beaches or even tropical forests? Have you ever thought about what is your footprint as an individual on this ecosystem? How this environment is affected by tourism in general?
We all know that today tourism is one of the most rapidly developed industries in the world. As economic power has been increased during last 50 years, population’s income also has been raised.
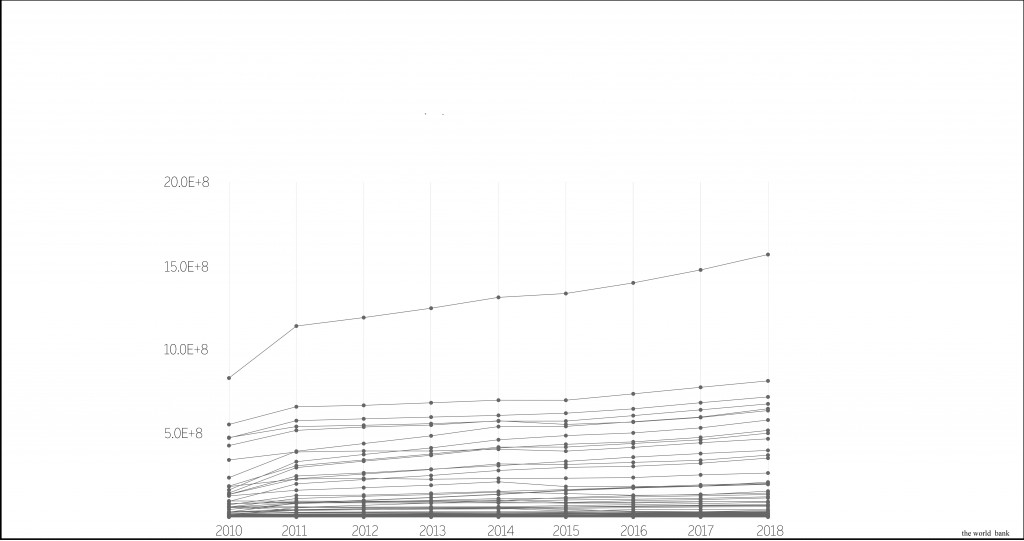
Growth of tourism in the world 2010-2018.
As we become more experienced and nothing can impress us anymore, we start to create new type of tourism.
Moreover, modes of transportation and technologic development allow us to achieve the most remote and delicate ecosystems. Phi phi island is a good example.
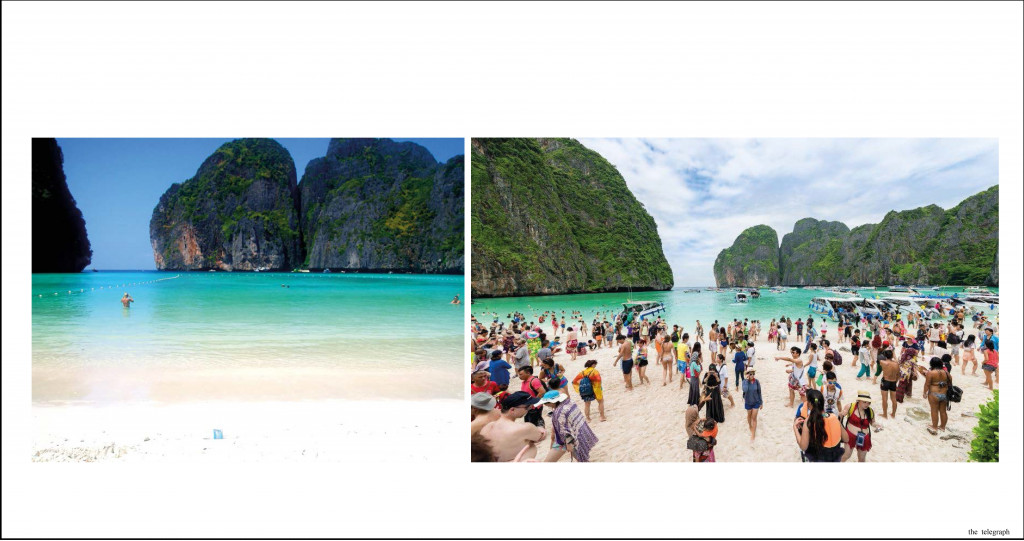

20 years ago nobody knew about it but today it becomes overcrowded every summer season. All ecosystems that attract tourists eventually face with enormous amount of waste, overconsumption of natural resources and wildlife disturbance. The obvious reaction of every government is closing the place.
However, is it a solution? Maybe there is another way to solve the problem?
The biggest issue is that we consume the environment in a very linear way.
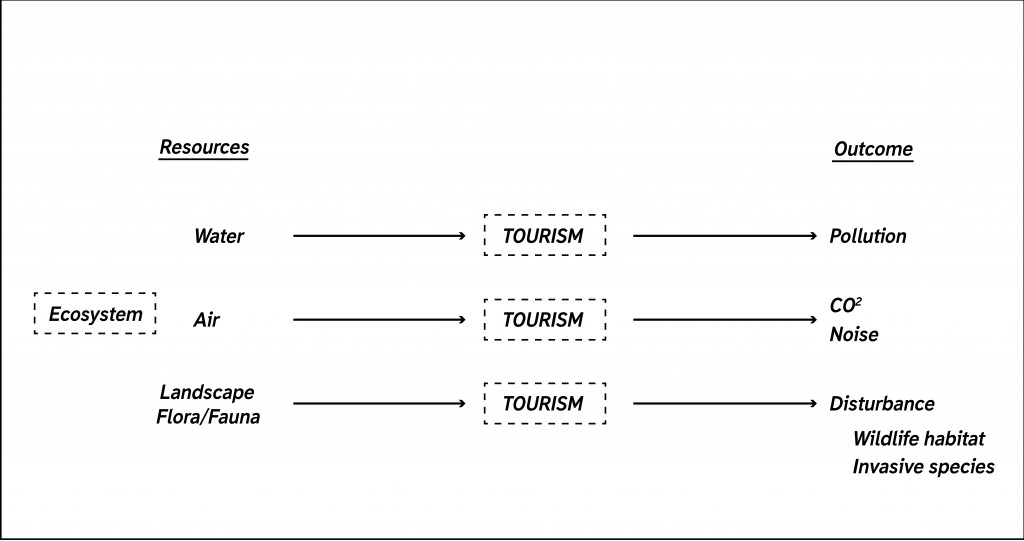
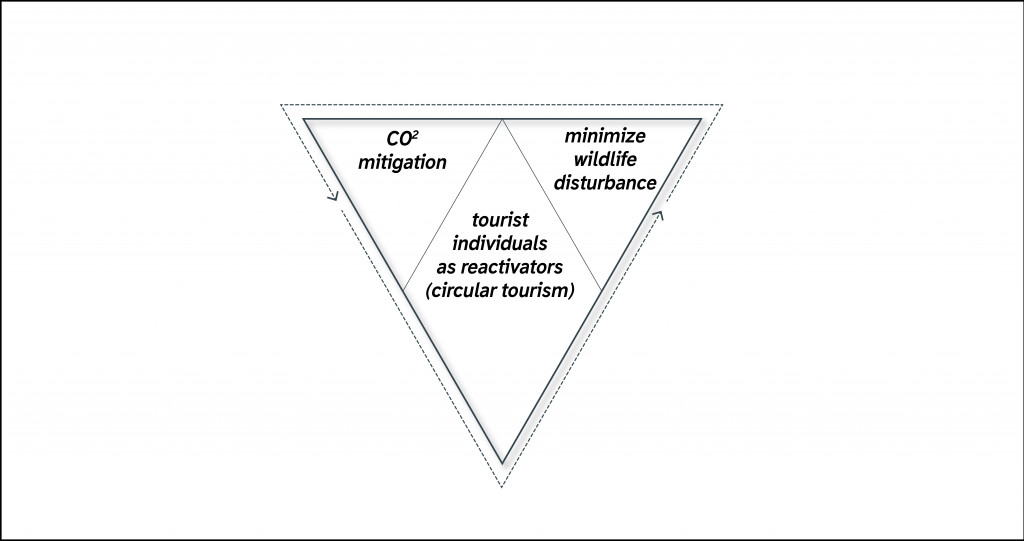
We take everything that place offers us, use it and don’t give anything back. The question is how we can jump from linear consumption to the circular one? How we can achieve the goal that tourist as individual and tourism as industry work in a circular way? Is it possible to use tourism as an activator of the delicate ecosystem?
Antarctica. Exploring one of the most specific ecosystems.
Antarctica, the icy continent that was firstly visited in 1840th today attracts more than 50 000 tourists every season.

Growth off tourism in Antarctica 1994-2018
The time that is appropriate to human beings here is limited.Visiting this continent during winter season that is in Antarctica from May to October is impossible due to weather conditions and absolute night. There is not a lot of ways to go to Antarctica. The easiest and fastest is the one that takes only 2 hours by plane. Actually, only 10% of people prefer that. There are several intercontinental airports that accept charter shuttles. The biggest one is In King George Island.
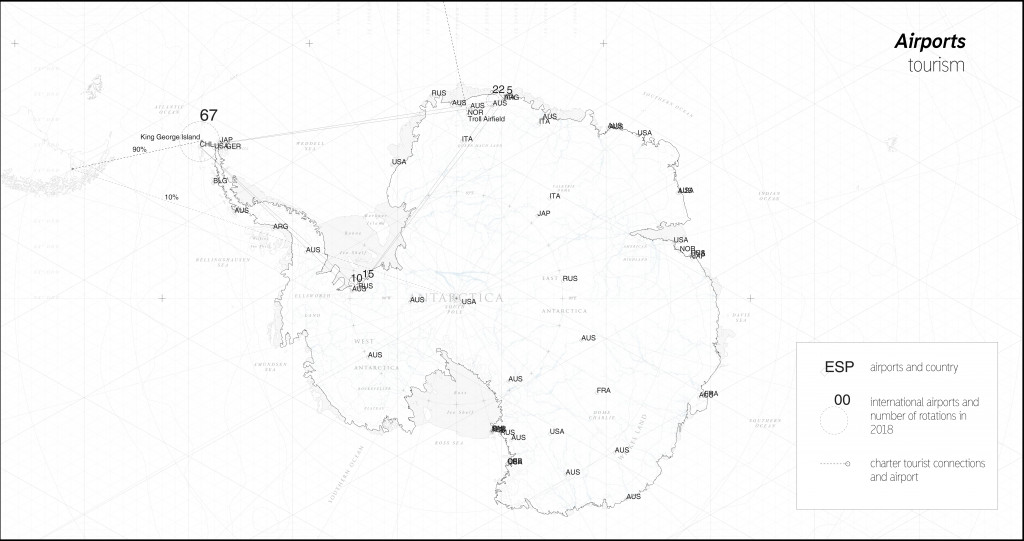
Intercontinental airports. Antarctica.
The other more attractive opportunity is the cruise journey that is offered today by more than 40 companies.
These routes are mostly concentrated in the Antarctic peninsula. Depending on the vessel’s capacity and trip duration we become responsible for enormous emissions. CO2 is estimated in tonnes per passenger.
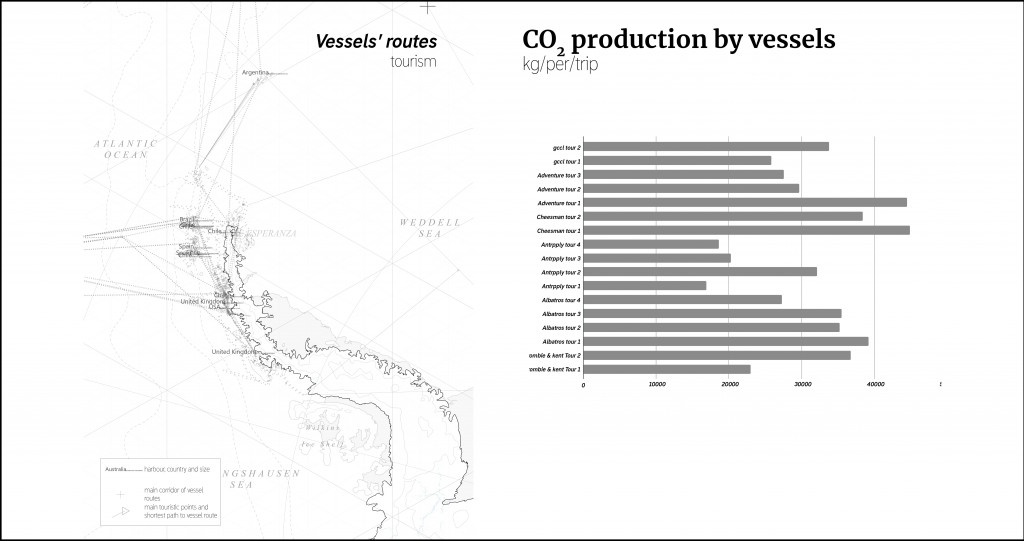
CO2 production per trip.
When you travel by vessel you spend on board more than 80% of your time. So, the tour operators that offer landing opportunities are very desirable. As the size of the ship is too big, most of them are not allowed to come close to the coast. So, all landings happen with small zodiac boats. There are a lot of landing sites on the peninsula. And this number rises over the years.
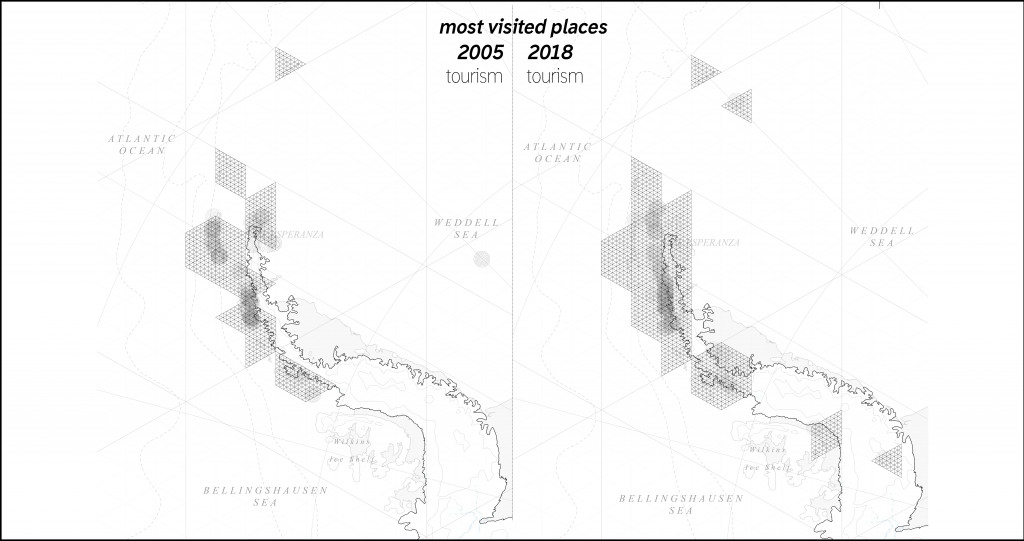
Difference in number of tourists landing sites.
But what is the purpose of these landings?
Antarctica is abundant with wildlife biodiversity. The food chain starts from phytoplankton through fish, birds and mammals. The first element is phytoplankton that is essential not only for Antarctica but for the world ocean at all. This small organisms consume 50% of all carbon emissions in the world. Which takes place at lower side of food pyramid It is also the main source of food for such creatures like krill.
Krill plays major role in the food chain, birds and whales rely on it year round. The population of krill decreases primarily due to uncontrolled fishing. And this circumstance creates obstacles for the next element in the food chain.

Krill presence pattern.
All penguins are concentrated close to the cost as the sea provides nutrition for them. Numerous penguin colonies attract tourists and disturbed by human presence close to their inhabitant areas.
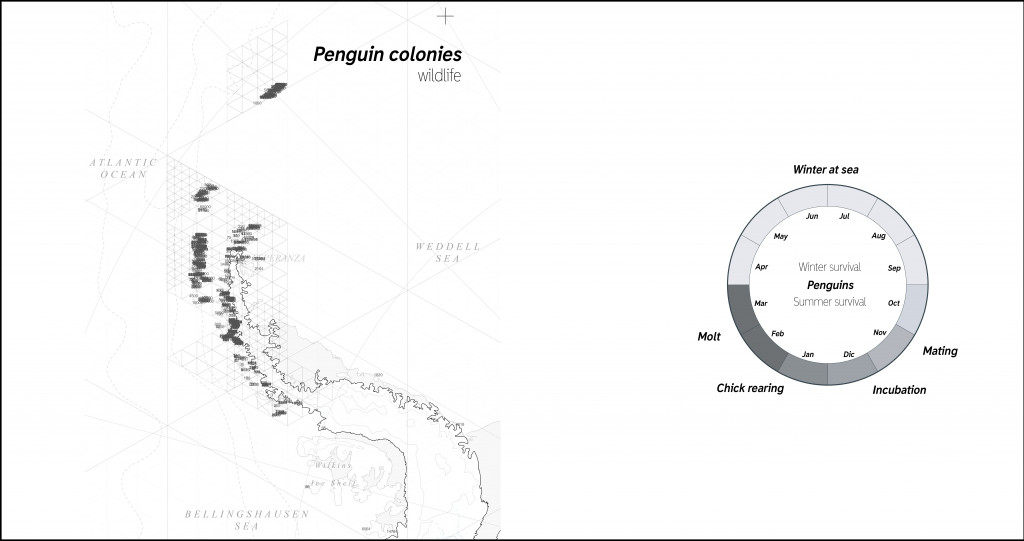
Penguin colonies.
Another species that are desirable to see are seals that also live close to the coast and migrate to islands to give birth.
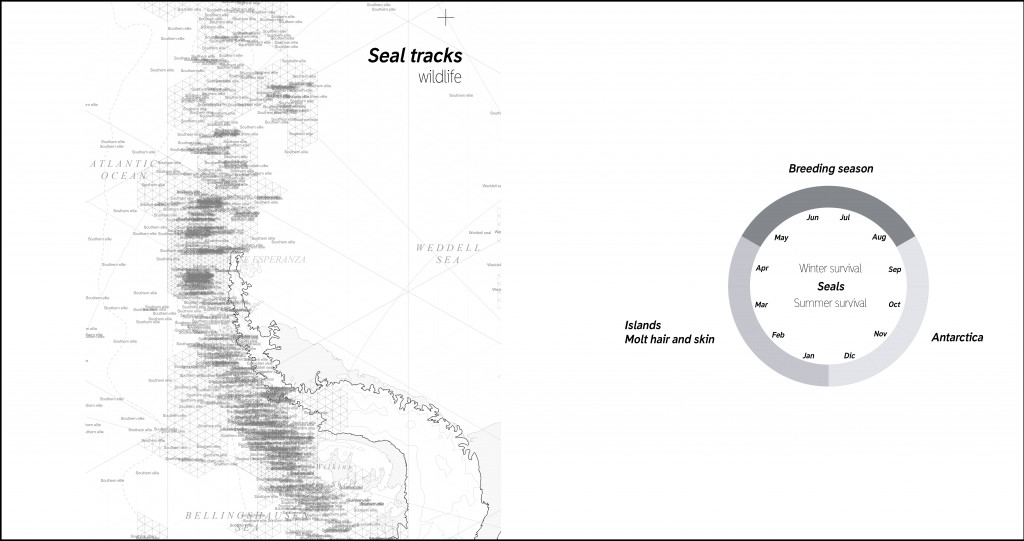
Seal tracks.
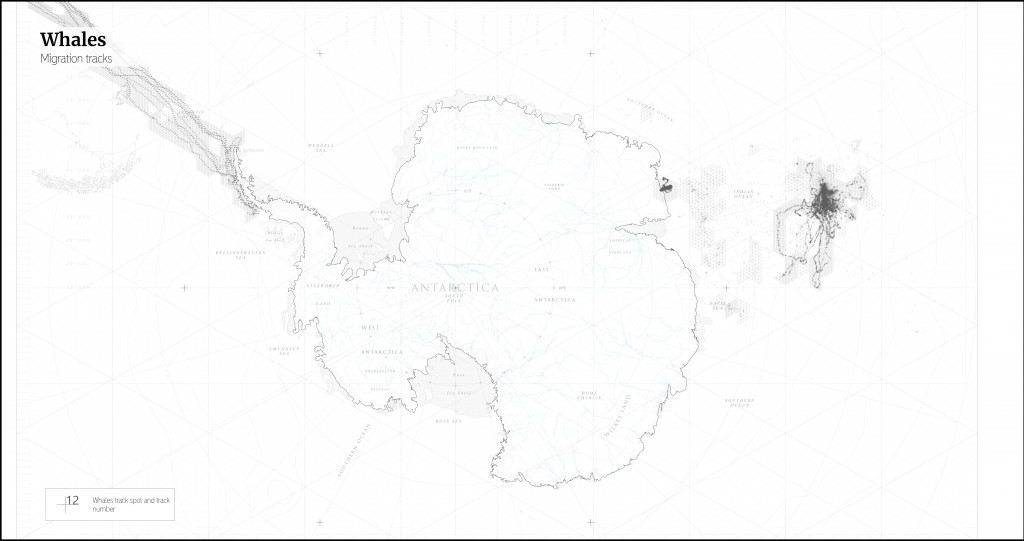
The biggest mammals that are most vulnerable are killer whales that’s migration tracks today coincide with vessel routes. All vessels produce underwater pollution and as operating in the low frequencies prevent whales to communicate properly.
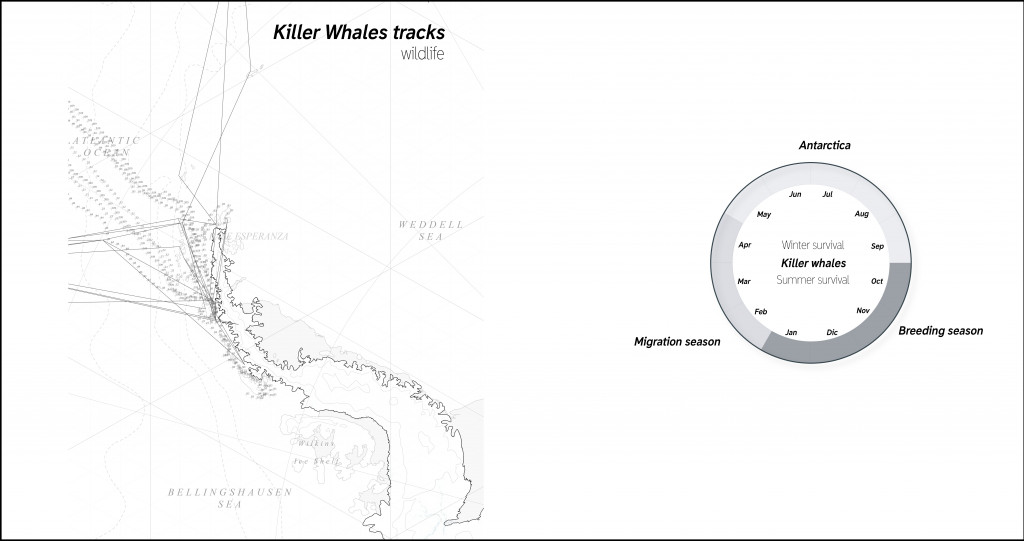
Killer whales tracks.
As we can see the problems that Antarctica face today are the same that other delicate ecosystem faces – pollution and disturbance. The strategy that can change the situation has to be strict and followed by all participants. Reducing Co2 emissions, decreasing wildlife disturbance and using tourism as an activator are the main goals.
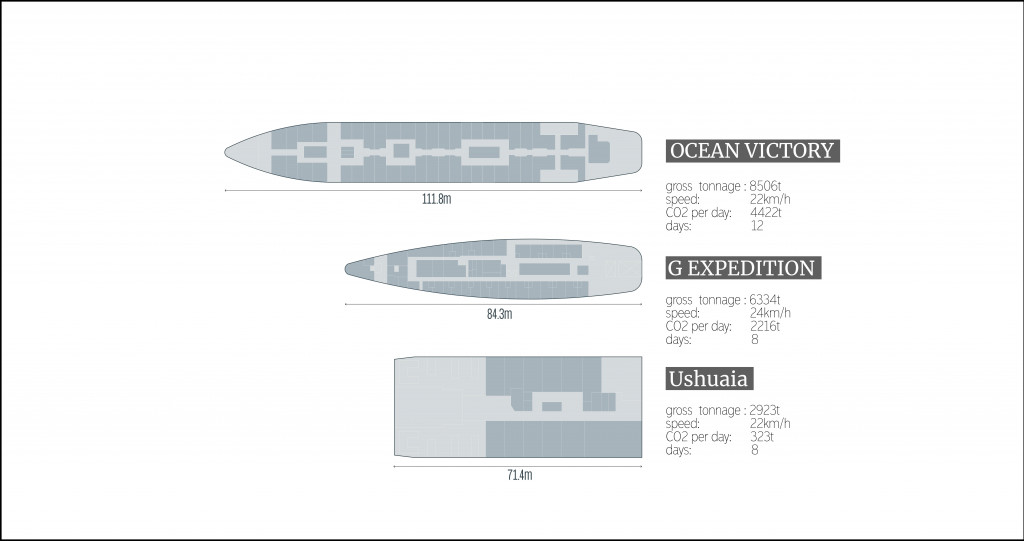
According to IMO objectives ( in frame of Paris convention in 2018) the CO2 production from maritime sector has to be reduced by 40% by 2030. The major emission production as we said before comes from vessels and depends on its gross tonnage, trip duration and covered distance. Here are some popular ships that are operated in Antarctica region.
For each of them we proposed the optimal route that will be shorter and less harmful for the environment and at the same time will be enough to see biodiversity of Antarctica.
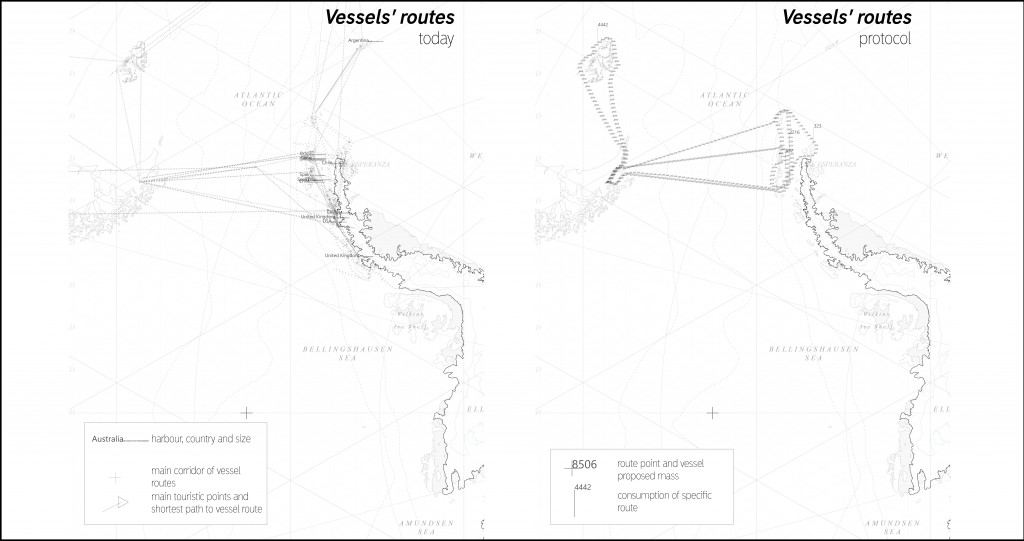
Proposed routes for vessels.
In order to minimize wildlife disturbance all vessels are banned to cross the whales migration routes. Underwater pollution will be reduced by decreasing speed to 10 knots when ships come close to the coast. At these speed ships’ propellers – the major noise creators don’t produce sounds that affect animals.
Protected area.
By using tourism as an activator we involve tourists at multiple stages of scientific research located at multiple places on the continent. Now all tourists who participates in activities such as kayaking, diving and polar plunge have to communicate with the closest scientific stations in order to help them in data gathering. Half of the time of these activities will be dedicated to scientific needs.
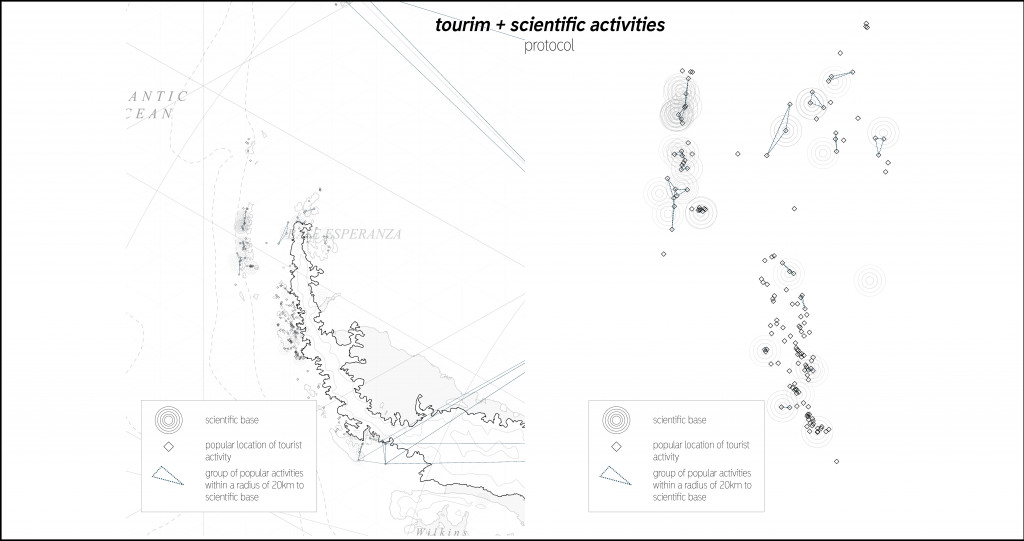
Cooperation between tourists and scientific stations.As far as we are concerned, these measures will help to change tourism impact on the Antarctica ecosystem.
Another urban context. Strategy implementation.
The tourism phenomenon happens everywhere around the world and impacts the local ecosystems. During the high season population of the delicate places changes dramatically.
This happens for example, in Palma de Mallorca island. The occupation of that place by tourists is enormous!
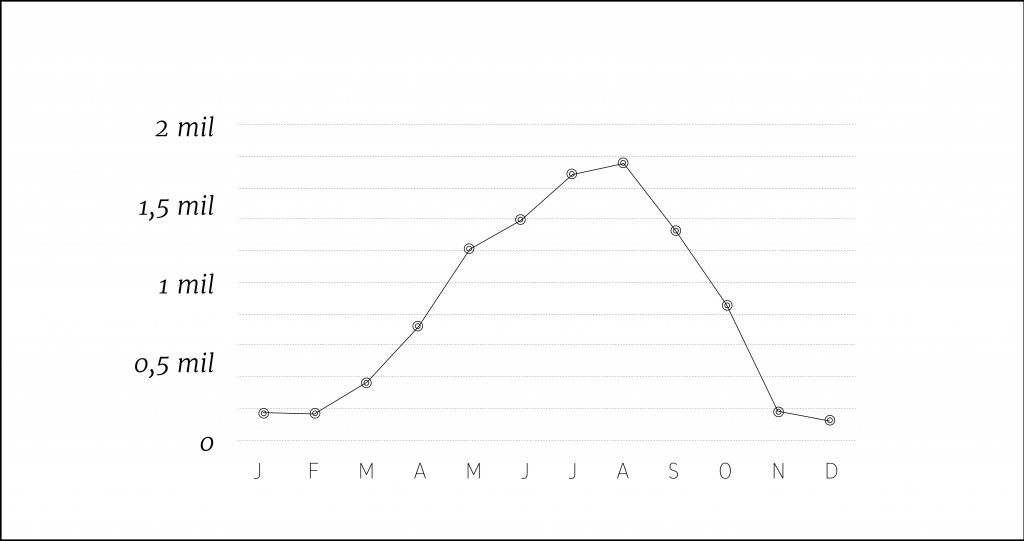
Seasonality of population.
Of course, nothing happens without leaving a trace. Existing infrastructure can not manage the load, as the pressure on sewage increases dramatically. This causes uncleaned wastewater to leak directly to the sea. As a result a large amount of waste appears in the beach and sinks to the bottom of the sea. The government reacts to this by closing the beaches. Similarly that we have seen In Maya bay. In addition, today we can observe the shortage of water reservoirs and underground resources that supply the whole island with drinking water.
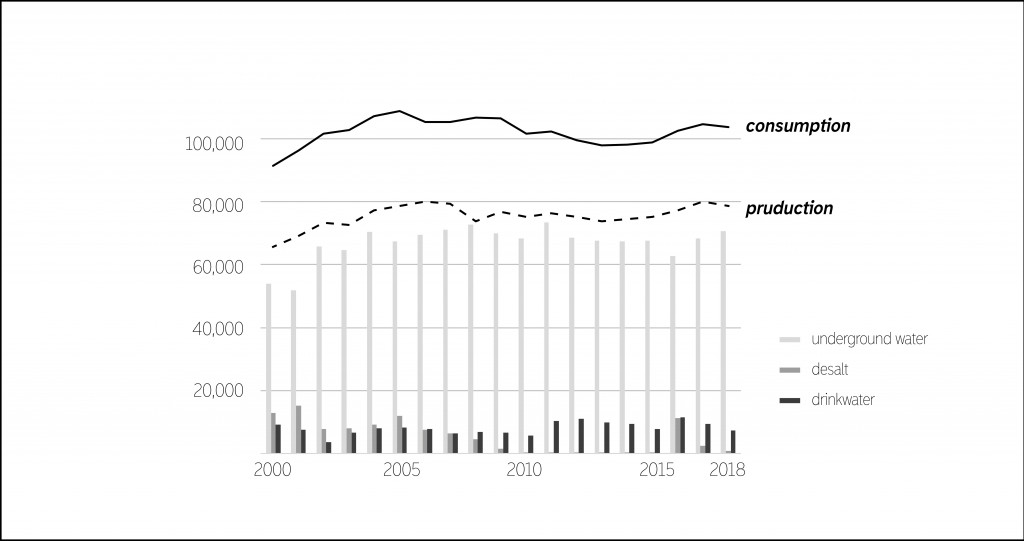
Water consumption and waste water production.
The strategy that was mentioned above is also can be implemented in Mallorca.
The European Union established the Drastic goal to reduce Co2 by 55% by 2030. This can be achieved by changing the policy on the island. Today, a lot of rental car companies operate in Mallorca. First of all, limiting the allowed vehicle categories like excluding SUVs and providing smaller cars that consume less fuel can help to decrease air pollution. The second step will consist of pushing companies to alter their vehicle fleet to 60% of electric automobiles by 2030.
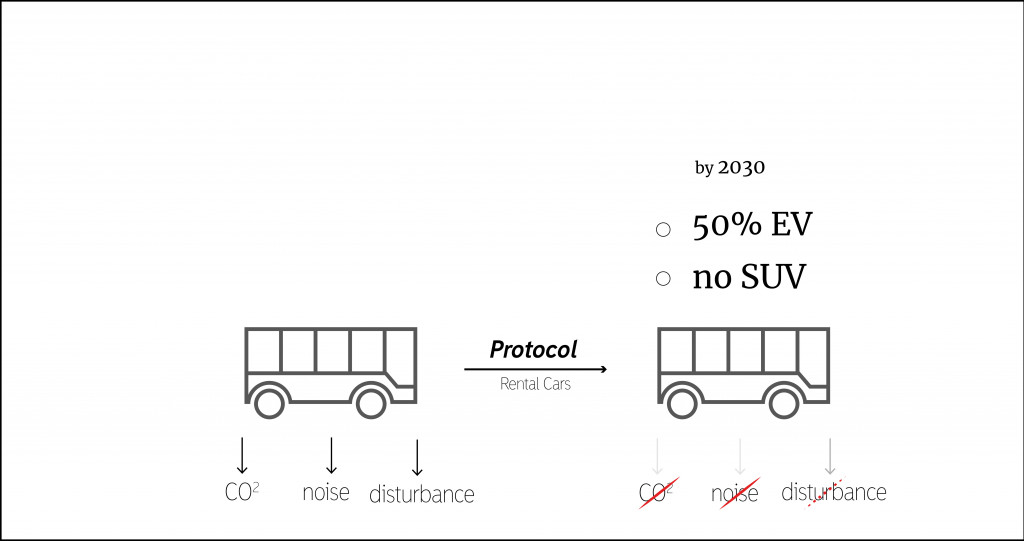
Strategy by 2030.
The city also has to participate in this process and set measures to supply gas stations with electric charger points.
In order to minimize noise pollution, vessel have to follow rules similar to Antarctica and reduce their speed when they come to the harbors.
On the other hand, to make tourism helpful to the city infrastructure, vessels’ water cleaning systems can act as an extension of cities infrastructure. The capacity of treatment installations of 500 vessels that arrive island every season is enough to maintain the local agricultural needs. The sewage storage tanker delivers wastewater directly to the vessel and after cleaning process this disinfected water goes back to the island.
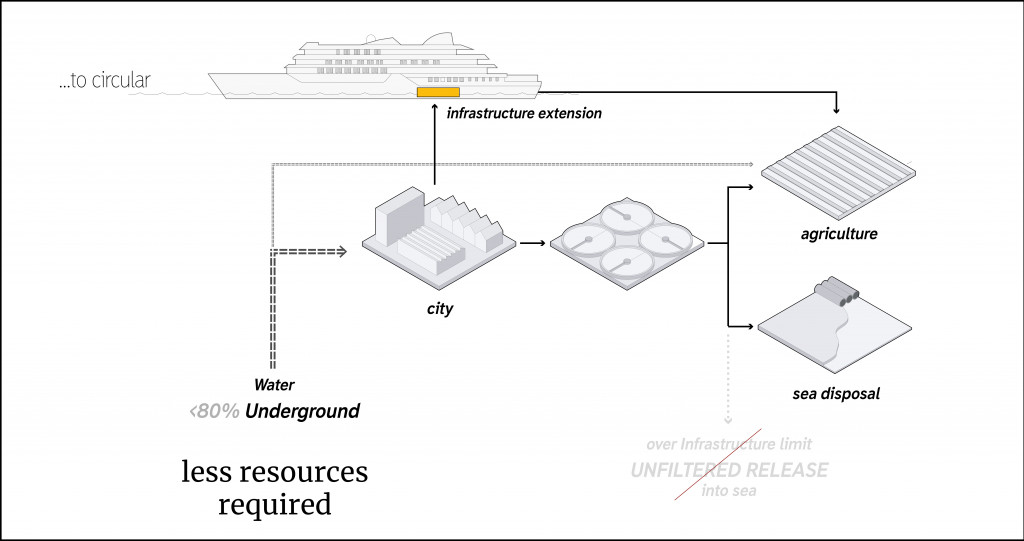
Ship as an extension of the city’s infrastructure.
All these measures will help to provide sustainable tourism development in the island.
Under such circumstances, in order to save delicate ecosystems and to prevent them from degradation that is caused by increasing tourism, human behavior has to be humble and grounded. Moreover, we have involve circularity not only to everyday life, but in all spheres of human being.
http://www.imo.org/en/Pages/Default.aspx
https://iaato.org/home
https://www.comnap.aq/Members/BAS/SitePages/Home.aspx
https://quantarctica.npolar.no/data-catalog/
http://www.antarctica.gov.au/
CIRCULAR TOURISM CAPITALISING ECOSYSTEMS is a project of IAAC,
Institute for Advanced Architecture of Catalonia developed at
Internet of cities, e.g. Master in City and Technology in 2019 by:
Alejandro Quinto Ferrandez, Akshay Marsute,
Jochen Morandell, Linara Salikhova.
Faculty: Mathilde Marengo, Edouard Cabay.