Context :
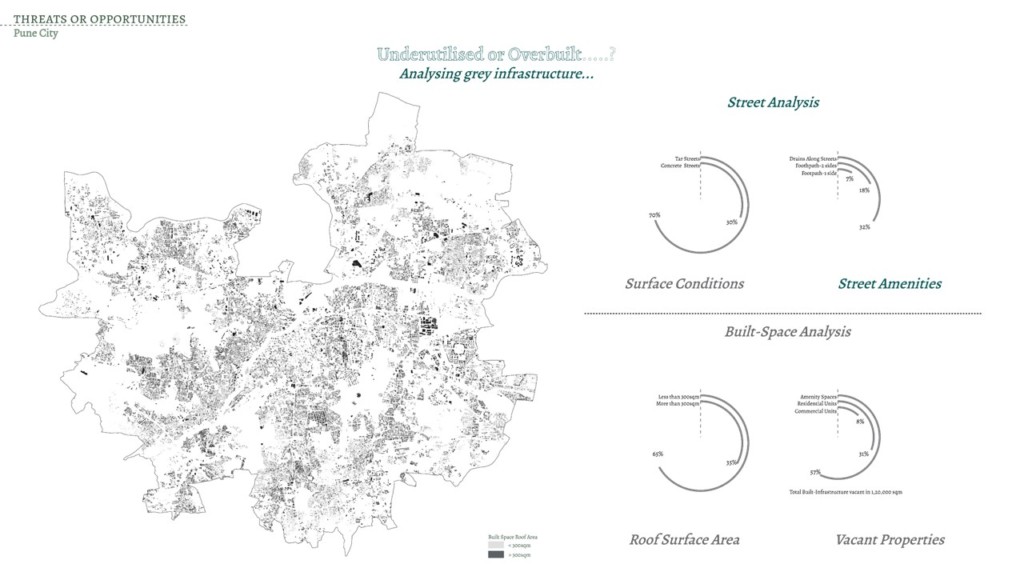
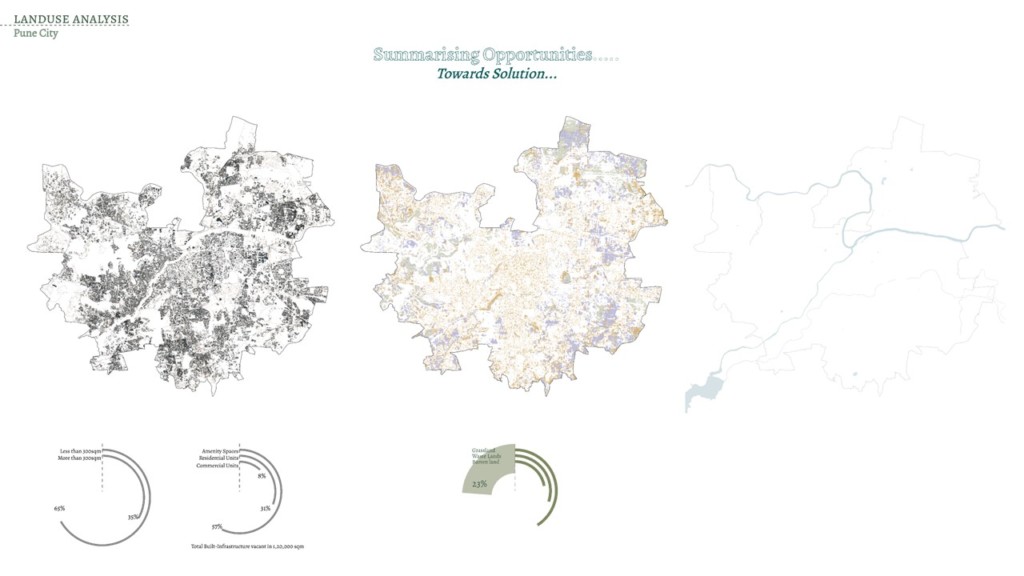
The global issue of climate change has pushed cities to revisit how cities are functioning and what are adaptive and mitigative pathways that cities can adapt. City of Pune in Maharashtra was studied to understand how the dense network of surface water bodies has effect of the cities micro climate. Due to limited data the experiment to use AI for Land use detection and understand the macroclimate around the waterbodies remained the main aim.


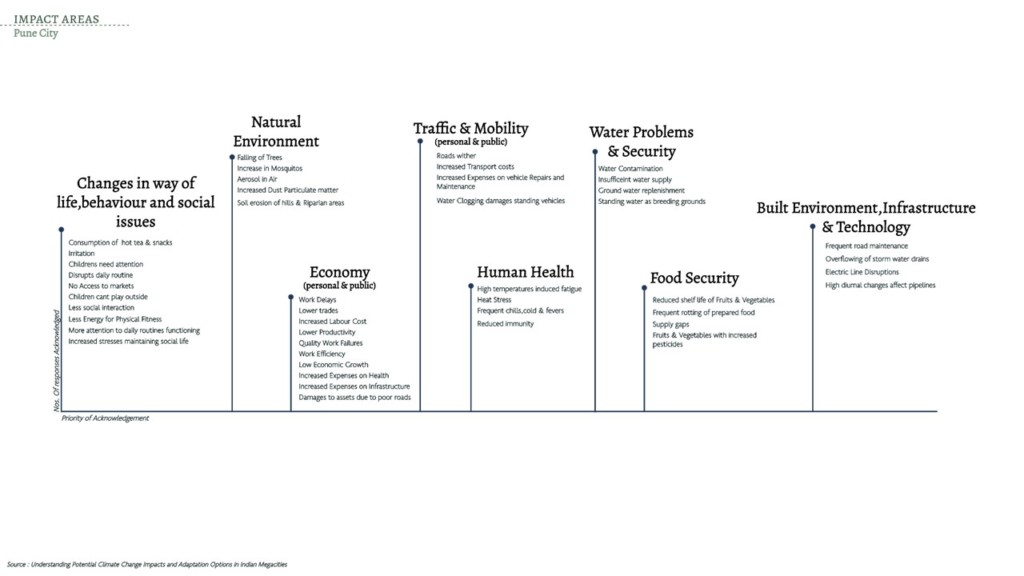
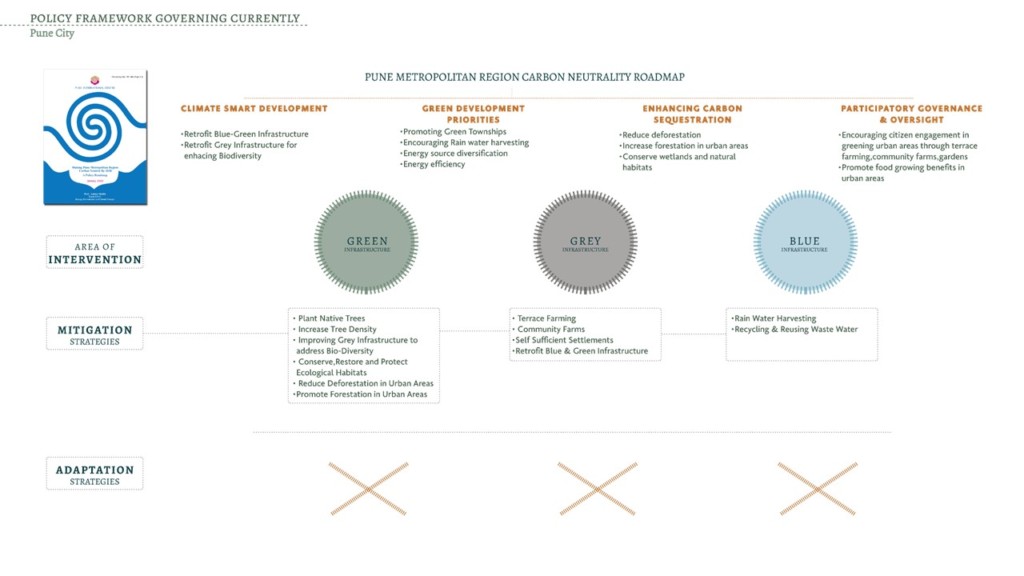

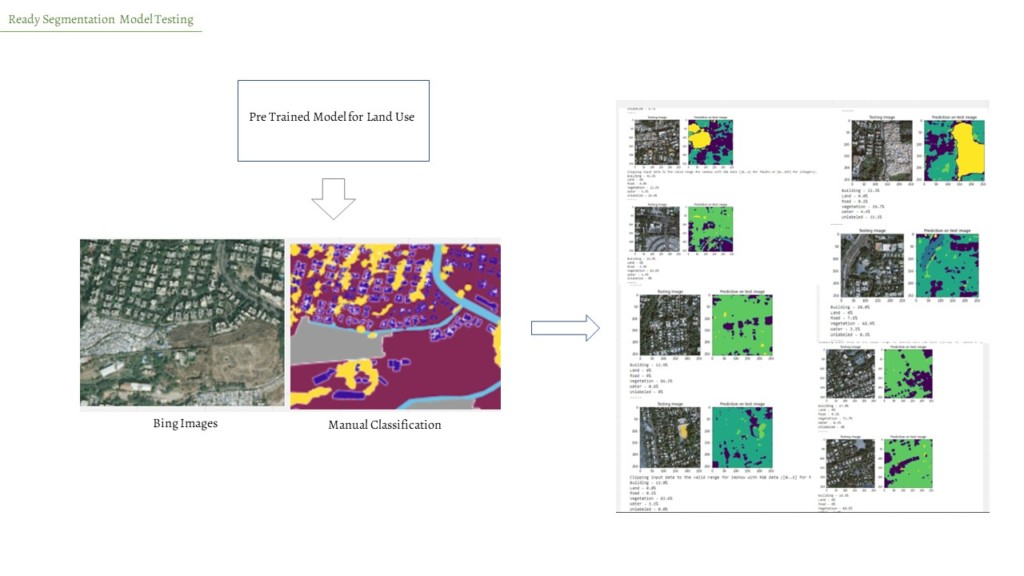
The land cover map from the ESA wasn’t sufficient to understand the city the in detail. Limiting to further analyze the impact of surface water bodies. Bing map images were highly detailed and it was possible to identify different land uses.
Methodology :
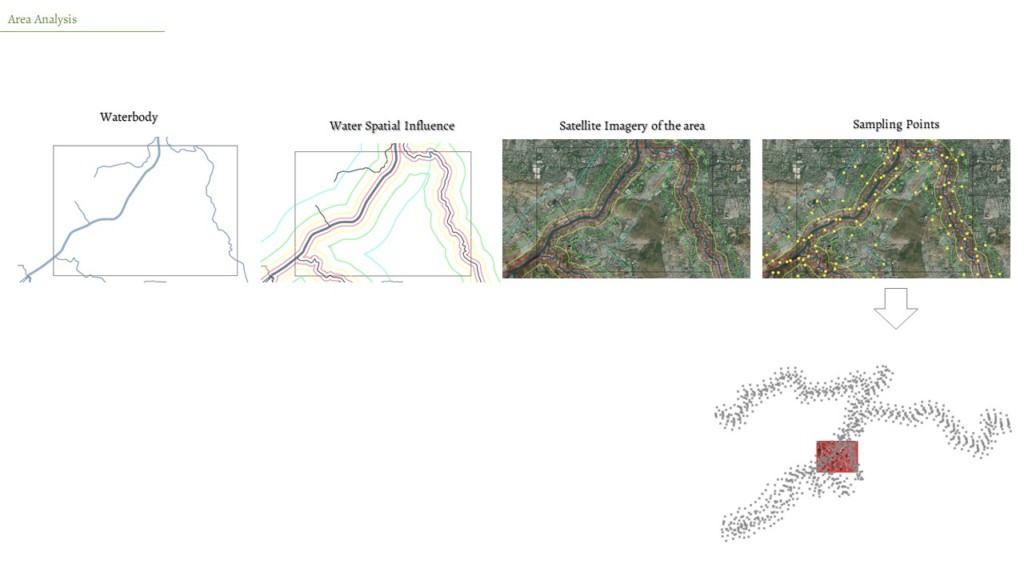
Area for the analysis was identified to around the waterbody. To understand the spatial influence of water around the surface water bodies, data points were sampled at 250m,500m and 1000m from the water body. The sampling points were use to collect different other data’s from remote sensed images like surface temperature and soil moisture to create initial dataset.
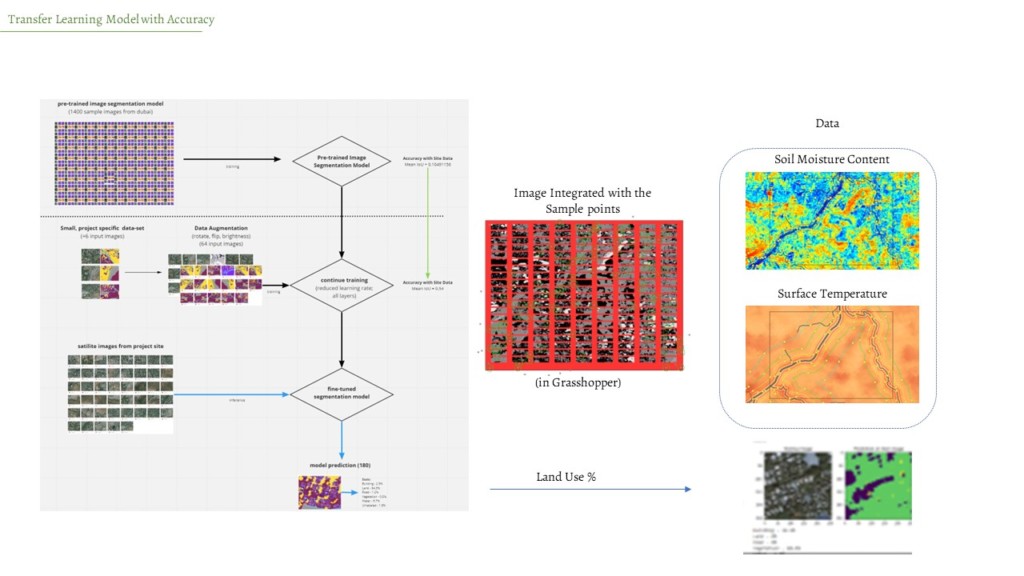
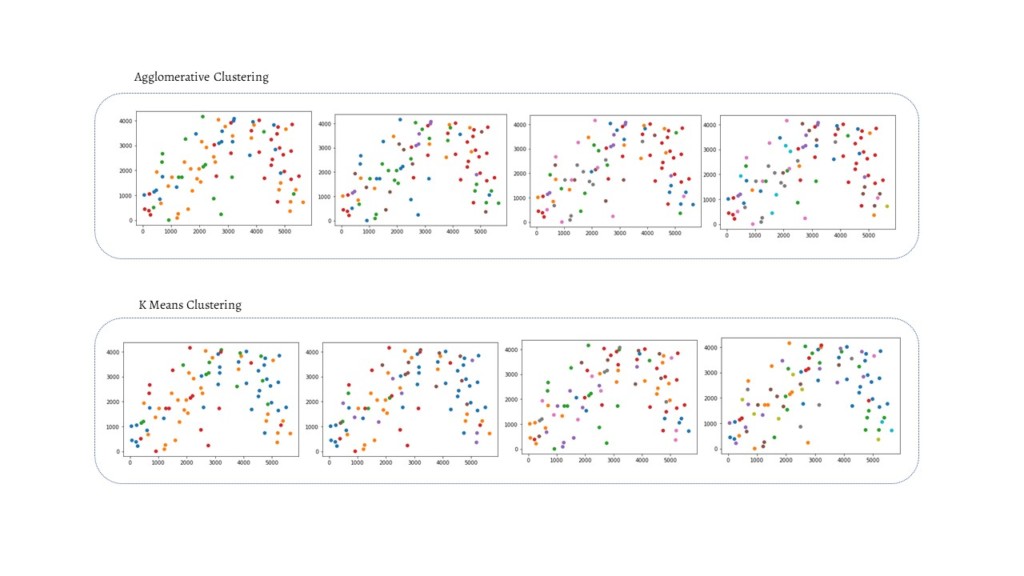
Sources :
AI for Climate Studies in Pune is a project of IAAC, Institute for Advanced Architecture of Catalonia developed at Master in City & Technology in 2020/22 by student: Kshama Patil and faculty: Angelos Chronis,Nariddh Khean,Serjoscha Duering