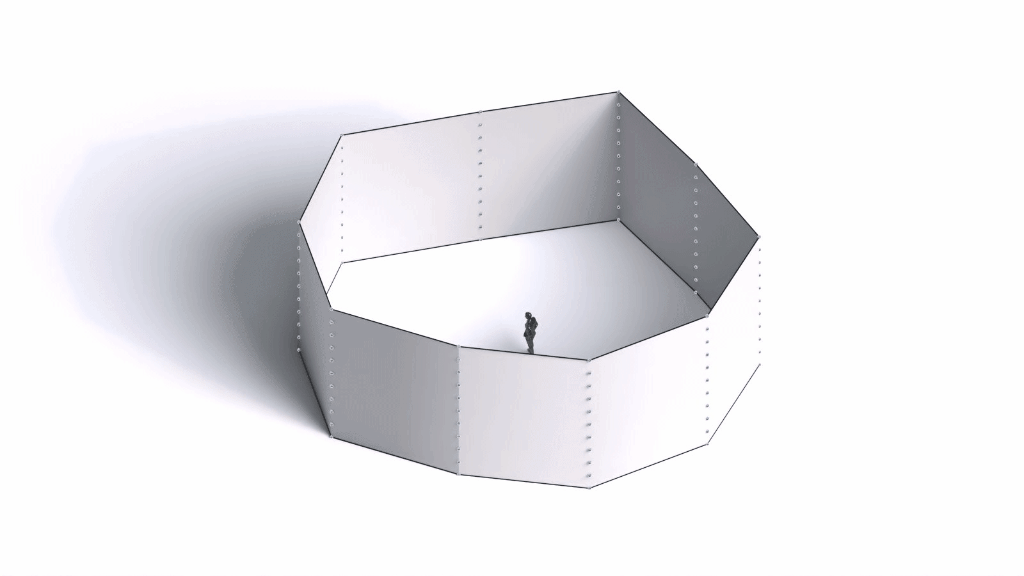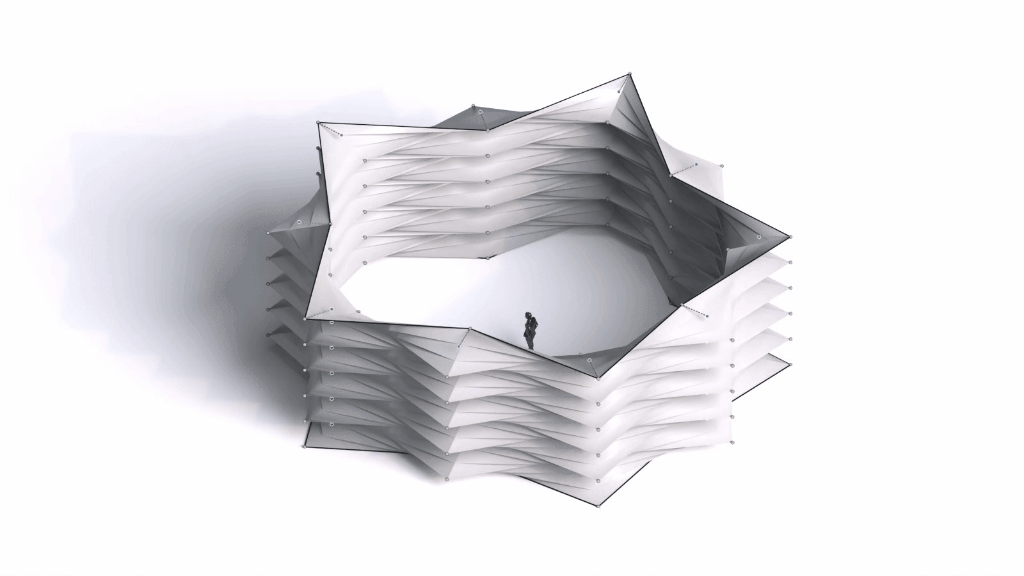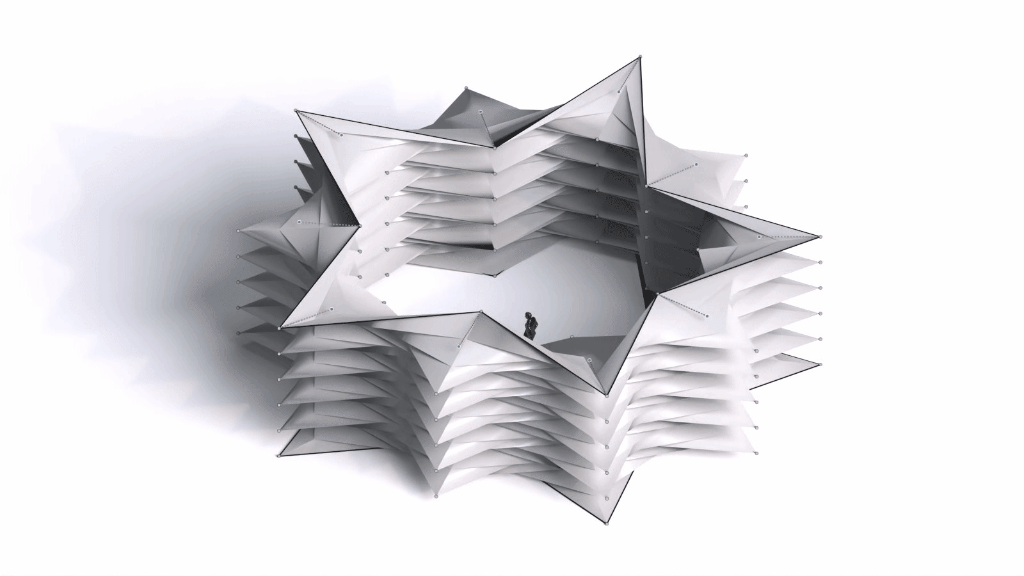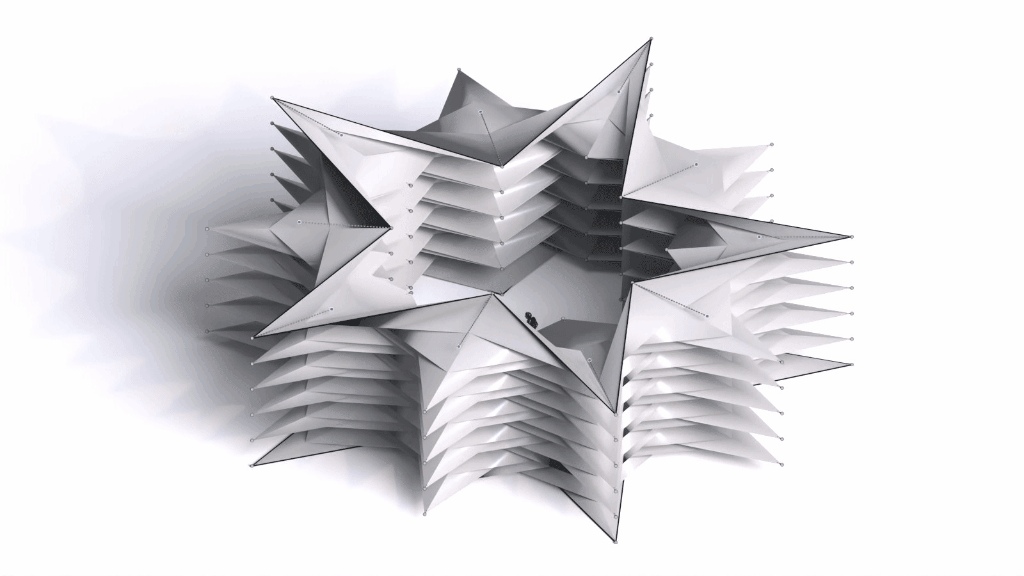
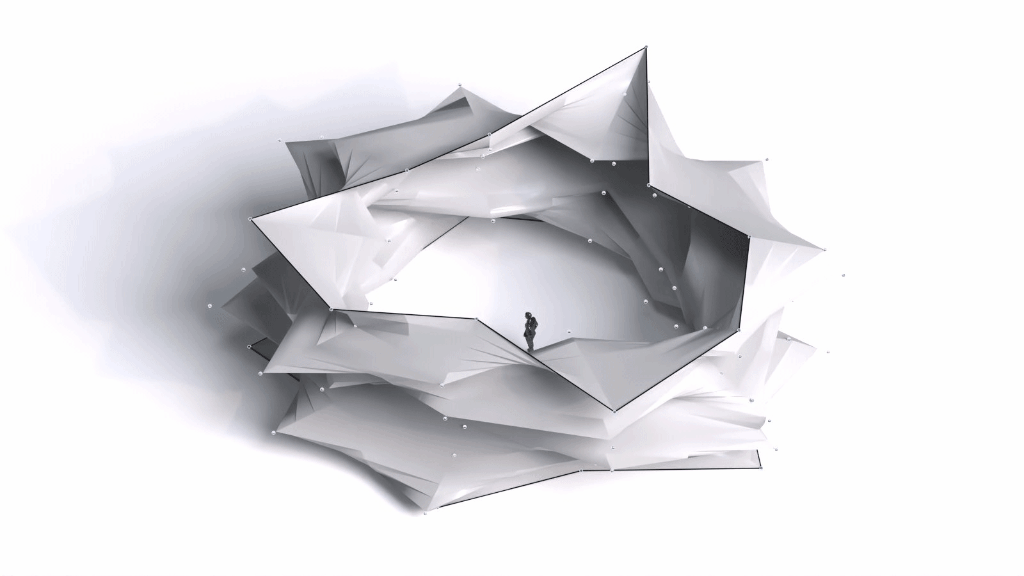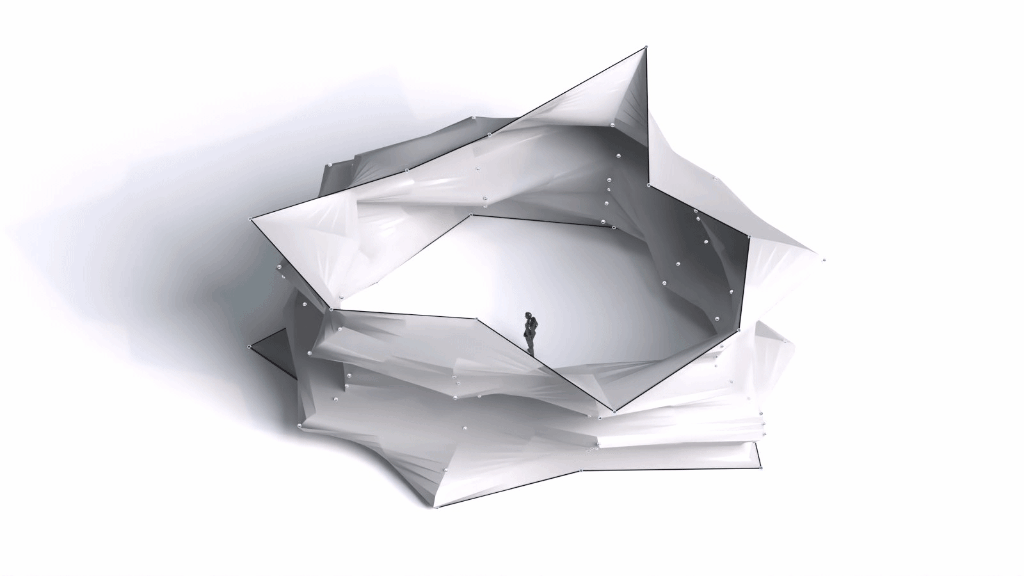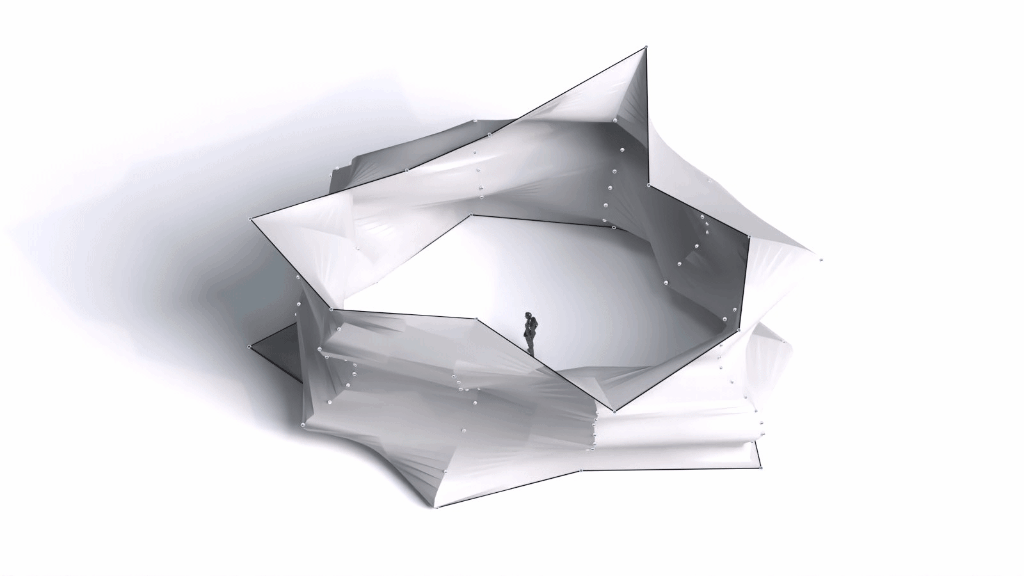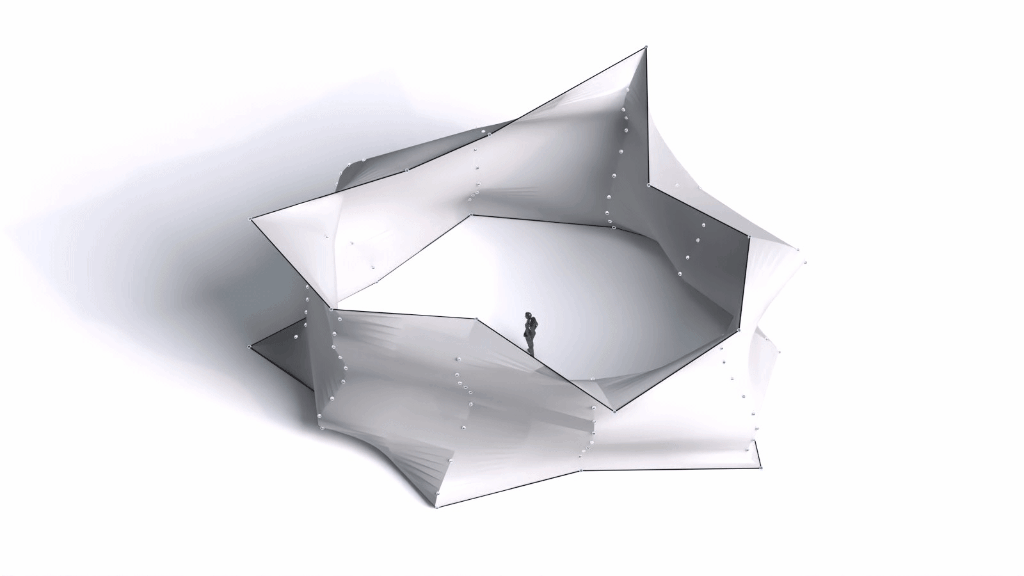
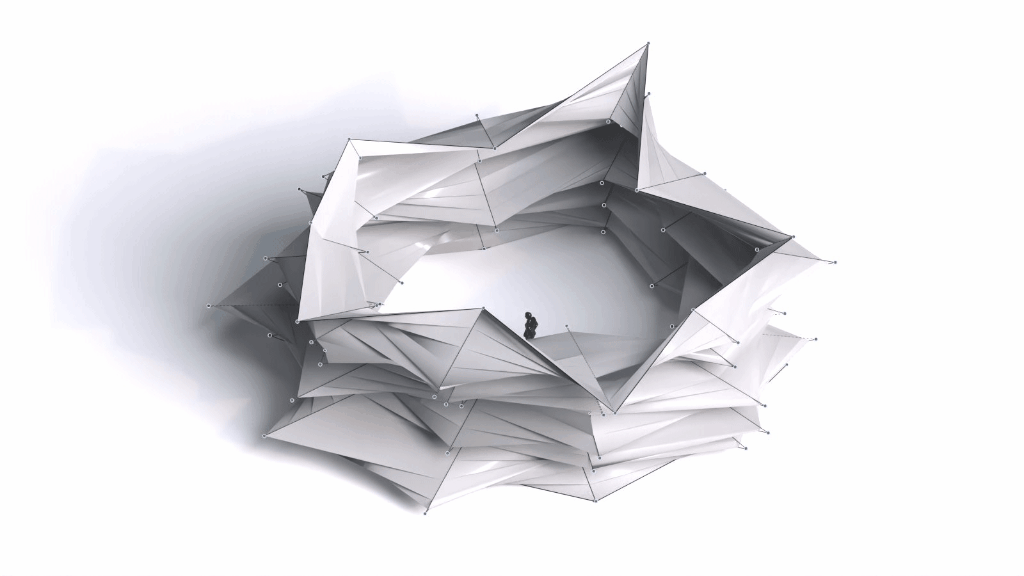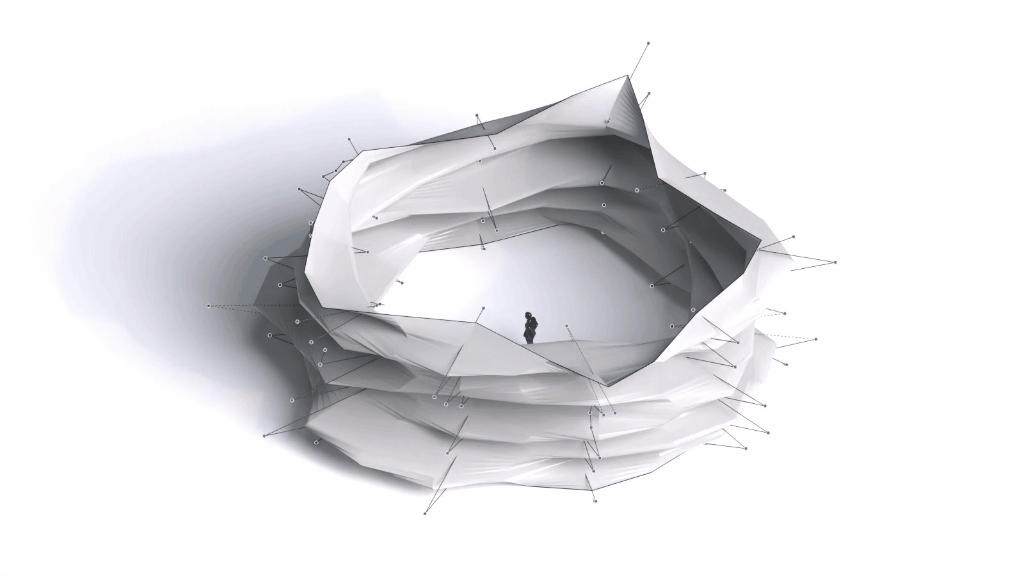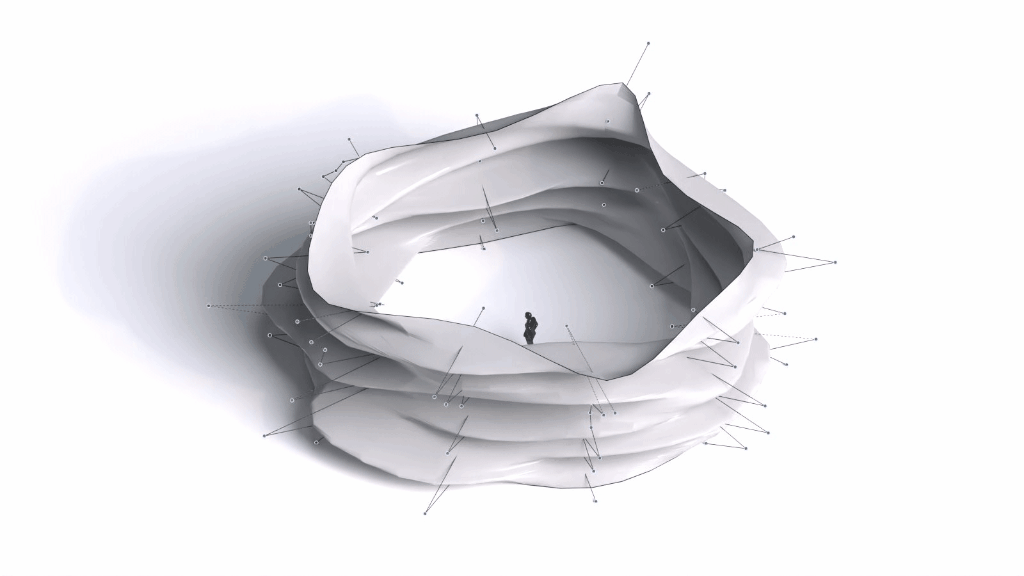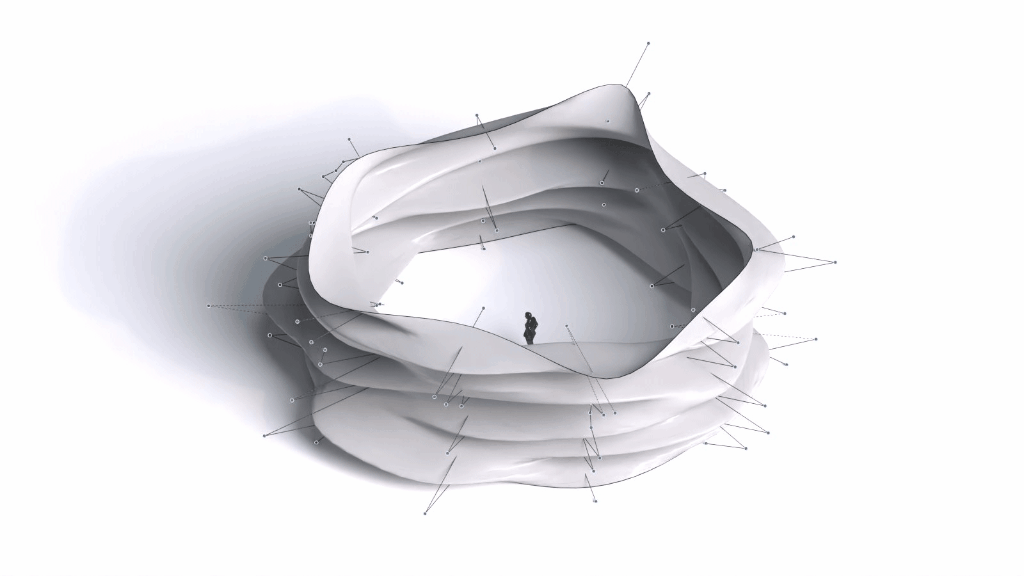
Architectural Intelligence
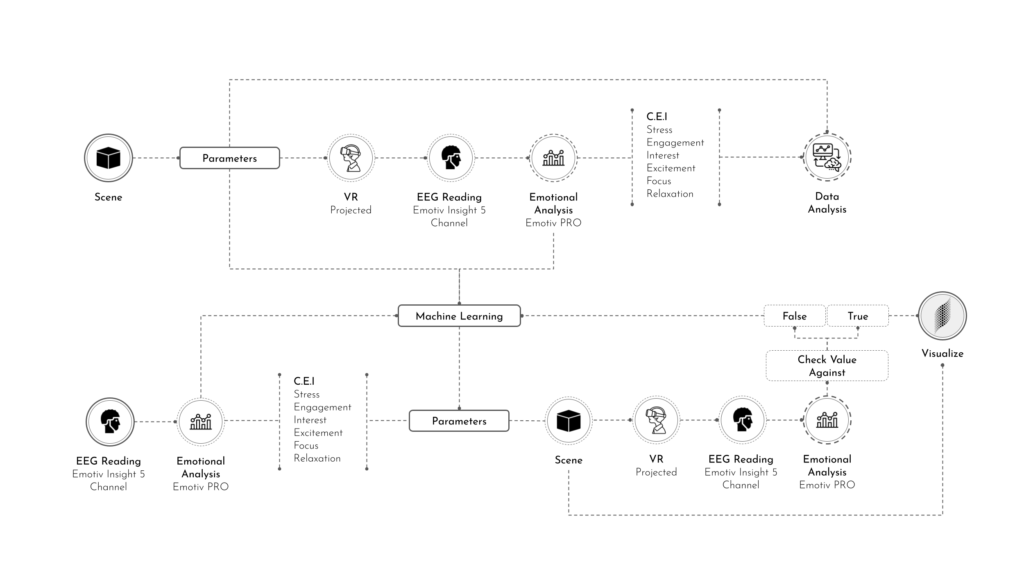
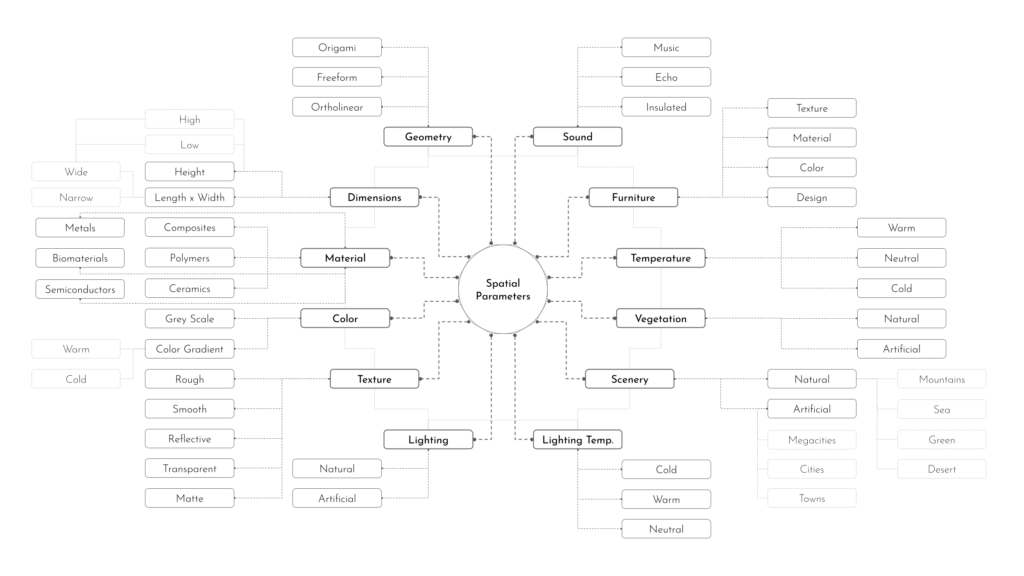
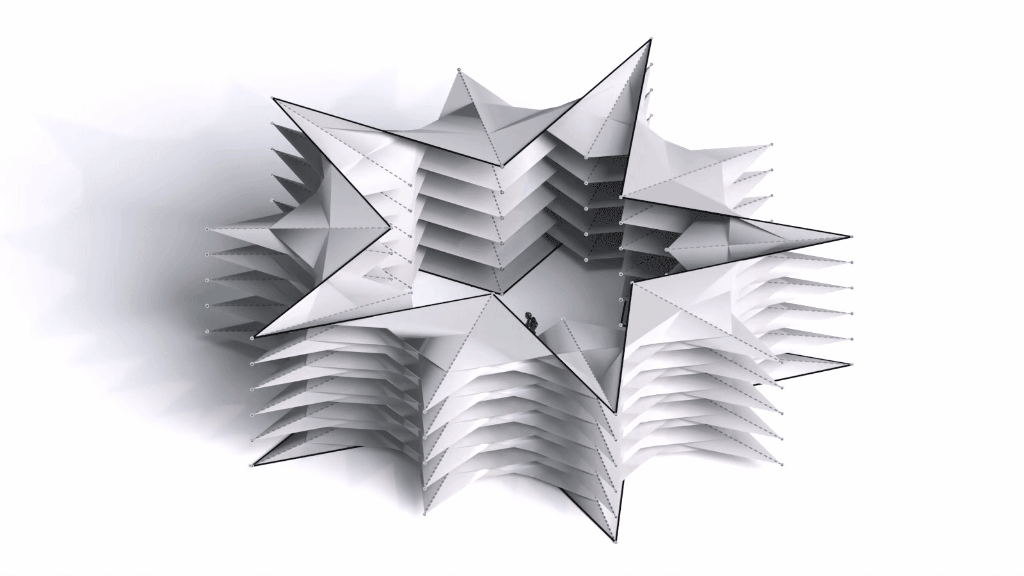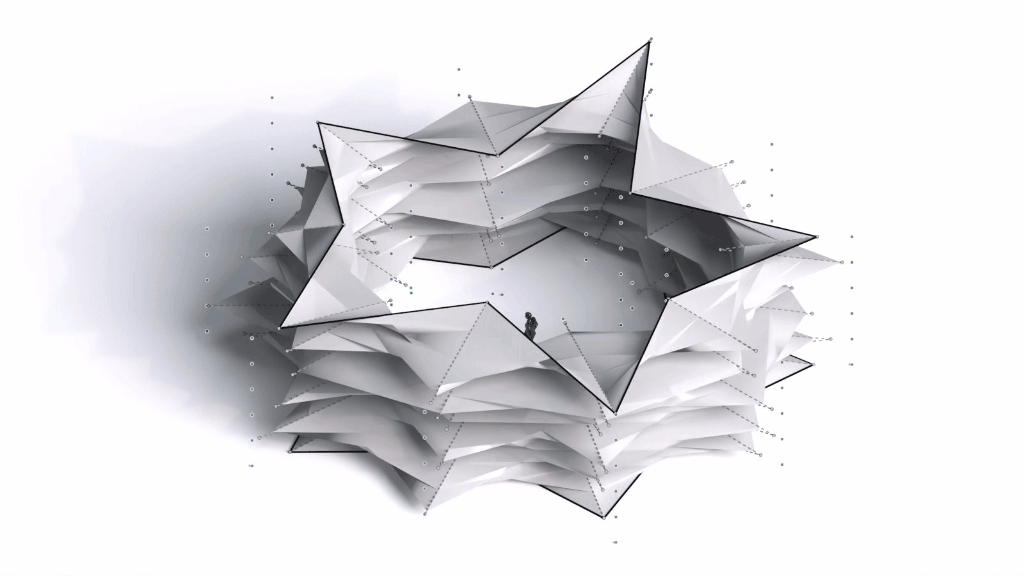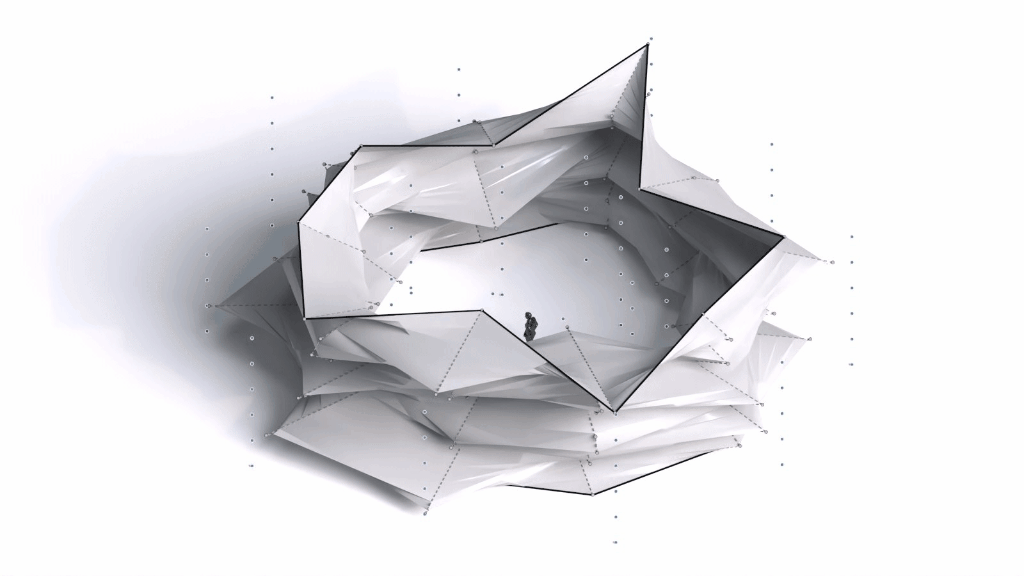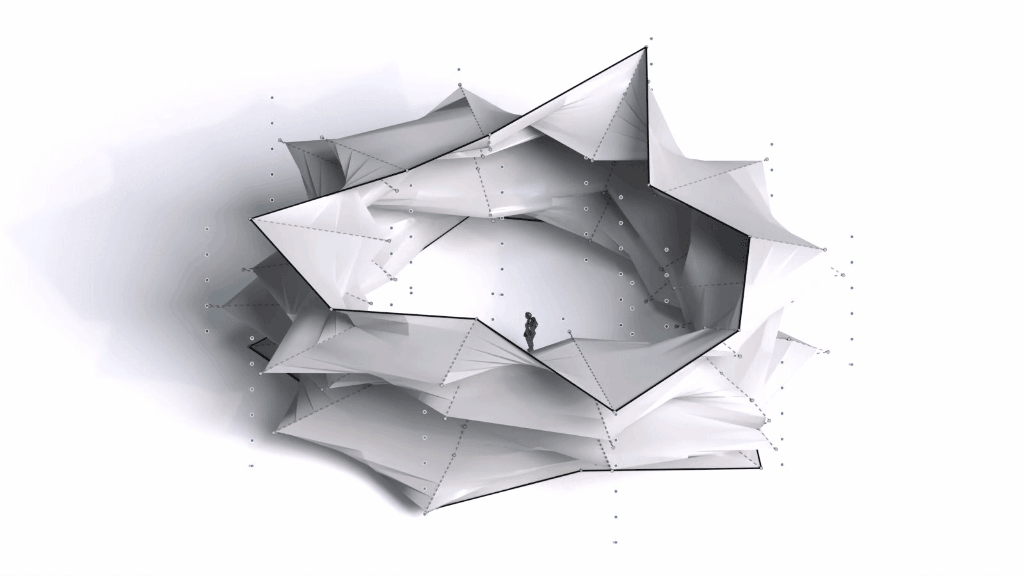
Architectural Intelligence aims to understand the relation between Architecture and Neuroscience, not only by studying the effect of Geometrical Spatial parameters on the users’ cognitive-emotional interaction (CEI) but also to reinforce and incentify the CEI by manipulating the geometrical spatial parameters with the aid of EEG and VR.
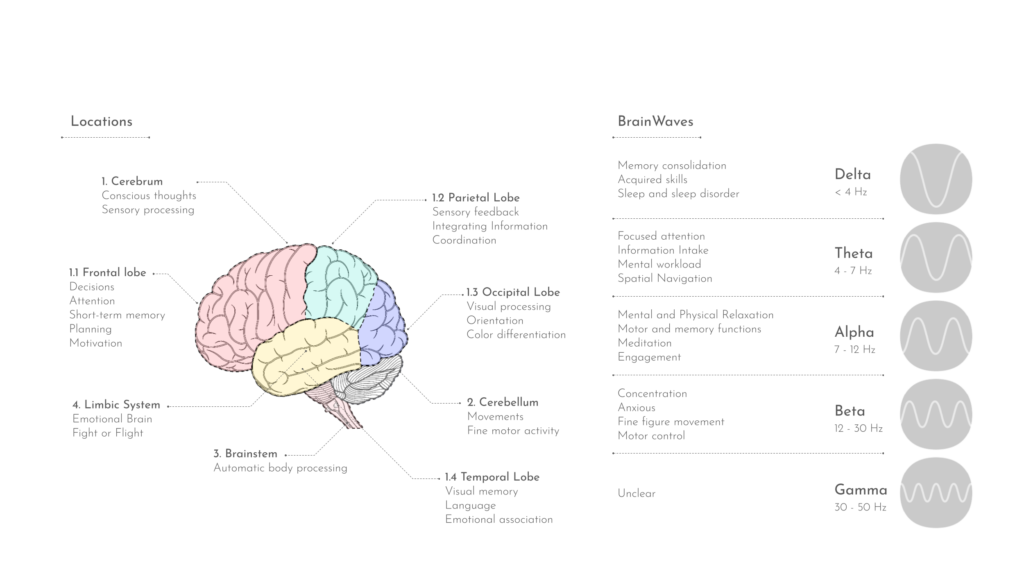
Cognitive Neuroscience
Neuroscience – Psychology
A multidisciplinary branch of biology and is the scientific study of the brain and nervous system. A broad definition, as is used here, includes the study of human thoughts, emotions and behaviour. It also seeks to provide a neural basis for behaviour and cognition.

CEI
Cognitive Emotional Interactions
Cognitive Emotion Regulation
The process of experiencing a certain Situation that stimulates a cognitive reaction (memory, attention, problem solving …) which then leads to an emotional response.
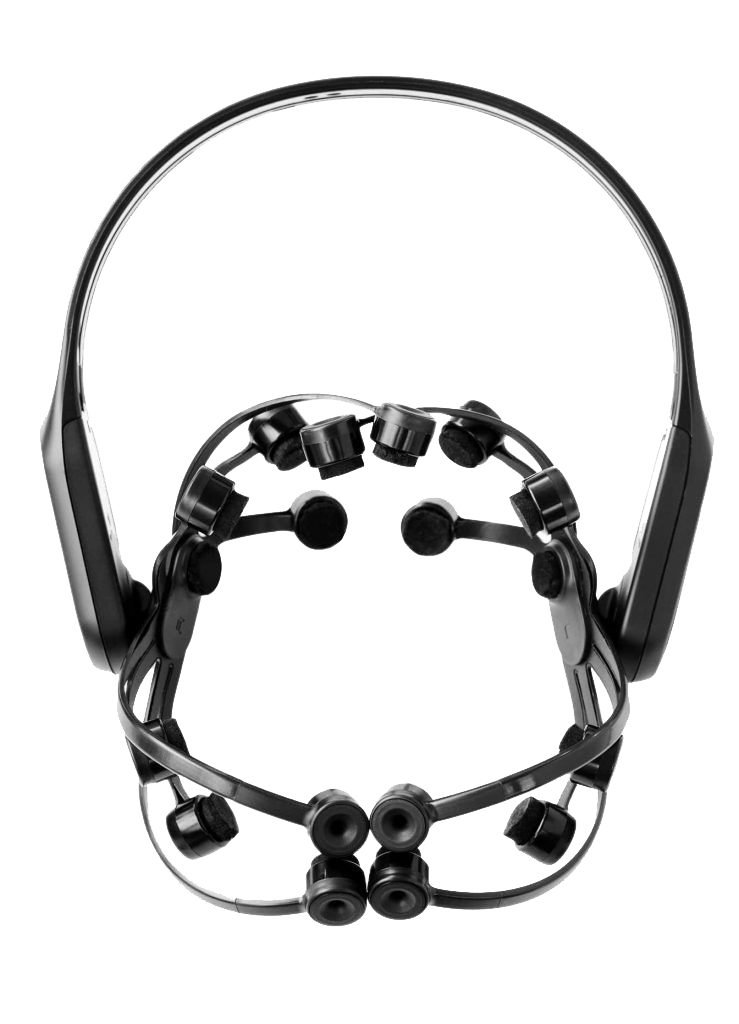
EEG
Electroencephalography
an electrophysiological process to record the electrical activity of the brain. EEG measures changes in the electrical activity that the brain produces. Voltage changes come from ionic current within and between some brain cells called neurons.

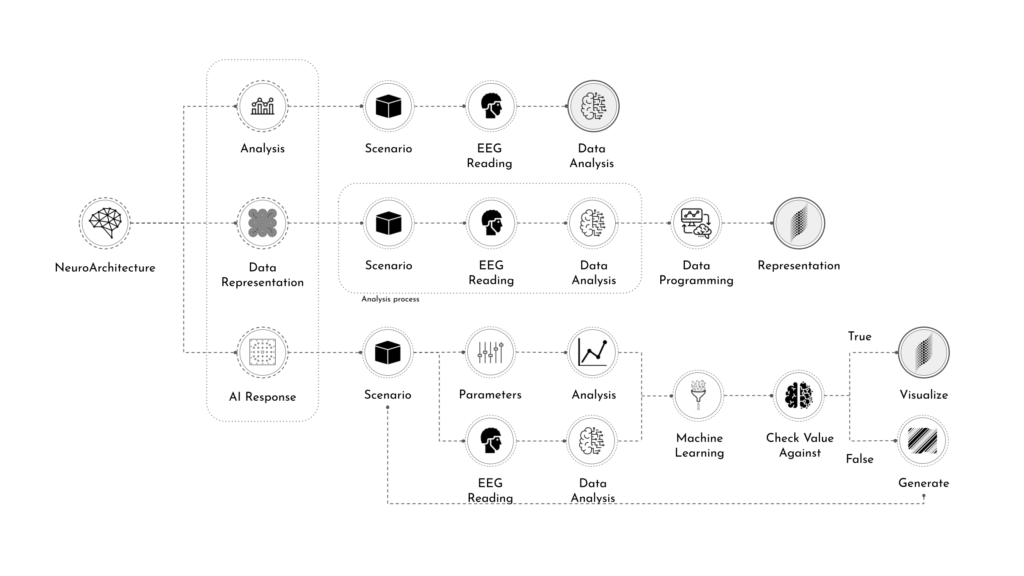
NeuroArchitecture
Neuroscience
Neuroarchitecture is a discipline that seeks to explore the relationship between neuroscience and the modern architecture design. By studying how the the spatial environment modifies brain chemistry, emotions, thoughts and behaviors.