CIRCULAR BIOECONOMY
Circular Bioeconomy – BIM – Mass Timber
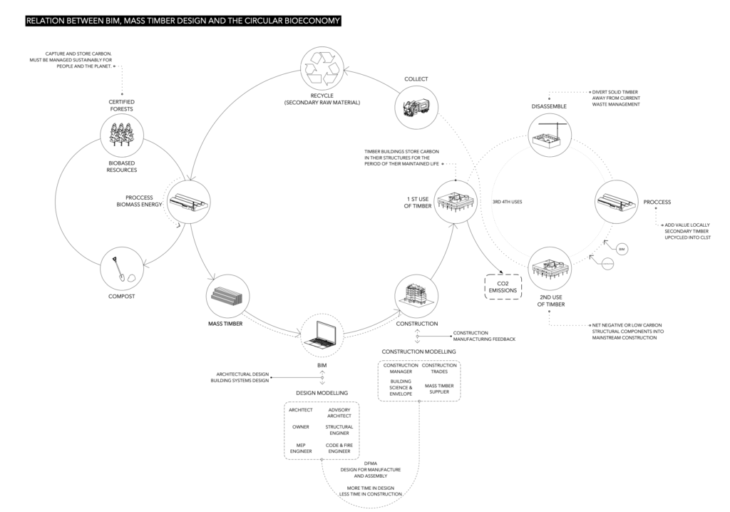
The relationship between BIM, MTD and the Circular Bioeconomy on a representative diagram of the Circular Bioeconomy, incorporates the BIM process and the M.T. in the flow. First the Certified Forests works as a biobase resource, which capture and store carbon. These have to be managed sustainably for the people and the planet. This raw material is processed in Mass Timber, which will be incorporated as a material in the architectural design elements and in the construction design system.
In the first design phase, the architect, the owner, the structural designer, and the different engineering specialists work together. The fact of using a BIM process gives more time in design and less time in construction (DFMA). After this phase there is feedback from the construction area, where the construction manager is working together with the Mass Timber supplier.
The first building built is the one that uses the first use of Mass Timber, which throughout its life will generate emissions and at the same time store carbon in its structure. At the end of its life cycle it will be dismantled, and the Timber could be disposed of as CLST. In this case the BIM process works again to build a building with the second use of the Timber.
Later this would be disposed of as waste and collected, and it could be recycled as secondary raw material. At the “end” it will to be processed as biomass energy and the emissions would be captured by the forests closing the cycle, while the waste could be treated as compost that would be the compost for the forests.
SUMA HOUSE

SUMA House
The main objective of the first module of the Tools course was to learn the basics of Autodesk Revit software. Based on a house made from Mass Timber by the architecture studio SUMA in the city of Madrid, Spain.
Circular Bioeconomy – Suma House – Tools is a project of IAAC, Institute for Advanced Architecture of Catalonia developed at MMTD in 2021/2022 by student Juan Bugarin. Faculty: Michael Salka. Course: MMTD01 – Tools