Book: Limits to Growth by Dennis Meadows, Donella Meadows, Jørgen Randers, William W. Behrens III
Topic: Bio-circular design
Extended Abstract
“If present growth trends….continue unchanged, the limits to growth on this planet will be reached sometime within the next one hundred years. The most probable result will be a rather sudden uncontrollable decline in both population and industrial capacity.”
Cagle cartoons, “Why we should care about population”
The book Limits to Growth tackles the most critical issue of the modern time which is human’s interaction with their finite environment. The basic idea of the book revolves around the fact that the resources of the planet are finite and can only sustain a certain number of population. After which it’ll be difficult for human race to exist on the planet and to avoid that measures should be taken as soon as possible. The main parameters studied for analysis are – Population, Industrialization, Food production, Pollution and Resource depletion. Emphasis is given on ‘interconnectedness’ between these and other major such aspects of a functioning world. Changes cannot be made by alternating just one aspect of growth and development because every industry and aspects of growth in the world are interconnected and changing one aspect for a positive result can lead to a negative result in another aspect.
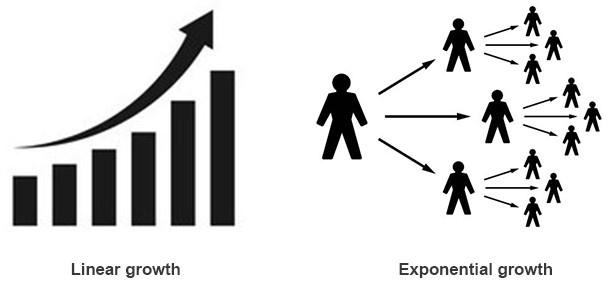
The book discusses certain standard factors which helps in better understanding the concept of growth. There are 2 types of growth – linear and exponential growth. We always think of growth in a linear way, which means it grows arithmetically (1,2,3…). Resources, Industries and Food for example grow in linear fashion. Whereas population grows exponentially (2,4,8…). That’s one of the most important things to know which is leading to a negative ecological footprint. Another interesting aspect discussed is the positive and negative feedback loop. It works like the compound interest growing on money. The more the profit, the more capital is available which eventually gives more profit than last time and vice versa. Population, Industrial capital growth have positive and negative feedback loop which has far reaching and long term changes on the world.
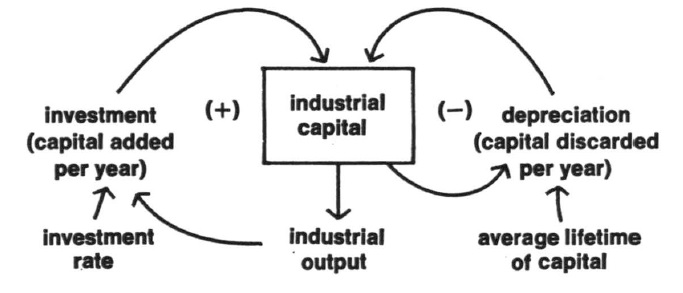
Positive and Negative feedback loop
The idea of the book has it’s base from Malthusian theory (1798) by economist Thomas Malthus. He suggested that population growth should be limited through abstinence and by restricting the marriage of those who live in poverty or suffer physical defects. He also theorized that disease, starvation and war were “positive checks” that helped to limit population growth. In the mid 20th century there began a revival of Neo – Malthusian, which has continued today through 2010s. It differs from the original theory in terms of use of contraception as the most practical means of limiting population growth. However, there are critics also known as Anti – Malthusian who believe that the human species has the capability to survive and sustain itself with a growing population, like the more number of people the more possibilities to find solutions to modern problems.
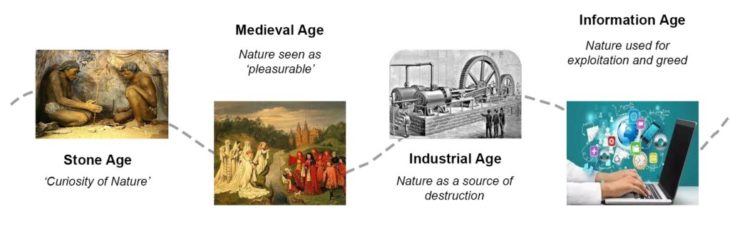
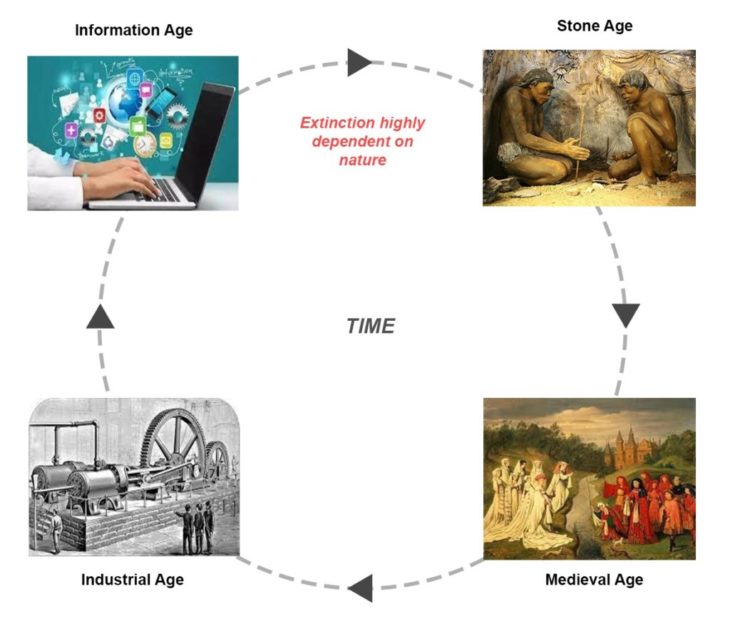
History of Man’s interaction with nature. Illustration: Kshitij Sarote, 2021
It’s interesting to know how man’s interaction has been with nature throughout history. In the stone age, man was very much integrated in the natural ecosystem, trying to figure out how nature works and how he can use it for his survival. With discoveries of fire with stone and invention of the wheel, it became clear that nature can also help ease the burden of man which has continued till recent times. In the medieval period, nature’s role was also seen as romanticism. It was celebrated and decorated in everyday life, and man began to take care of nature for pleasure. Then came the ‘industrial age’ which had the popular idea of ‘positivism’. It was the time of great optimism about the role of science in Anglo-American and continental European thought. It began as a movement designed to marginalize religion and strengthen the role of science in society. Great scientists and inventors started looking at nature as a source of knowledge and started experimenting with it. Soon nature became the source of destruction, evidence of which could be seen in World Wars. Post World War, human life gained more value which led to fewer wars. Now the role of nature slowly began to shift towards advancements in human life. All sectors started to equip with technology leading to an easier and longer lifespan for humans. With the absence of wars, the only dominant factor for the decline of the human race as we discovered in recent times is ‘pandemic’.
The book kind of makes us paralyze by providing opposite but true ideologies. We agree to certain extent with Malthus, which gives us a warning and a precautionary alarm about how our actions can lead to our own demise. Which in fact should be taken into consideration and the development and use of resources should always be kept in check. But we also feel, as humans, man has always had the urge to explore and expand his territory. The stone age man has moved places in search of food, and so the kings moved around the globe to discover the ‘unknown’ to ‘grow’ their kingdom. Explorers and scientists too have looked beyond this planet and explored possibilities of a completely different world. At each age, they were doubted and criticized about their approach, but it always takes a handful of humans to decide the fate of the rest of the generation.
Cycling nature of Human Evolution. Illustration: Kshitij Sarote, 2021
The existence of human beings has always in one or other way made changes to the flow of nature. Especially after the Industrial revolution in 1800, there have been drastic changes to the natural ecosystem with ‘development in technology’. If we look at history, the span at which the changes are taking place in a short time. There have been more changes between 1900-2000 AD than 1000 – 1900 AD. Today the focus is being put on sustainability and implementation of bio-circular design aspects in almost all aspects. Though growth takes place on each level of the society, it starts with an individual’s urge of having more and growing beyond his present condition ‘physically’. It expands from family, to organization, city and so forth. That desire to explore today has led us to space explorations with focus on inhabiting a different planet.
Levels of growth:
- Individual
- House / Family
- Organization
- City
- National
- Global
- Planetary
The definition of growth has always been about ‘adding’ and expanding for progress. The focus today is been on reducing or ‘subtracting’ on use of resources and consumption for better future (progress). The change starts with individual choices and decisions one makes while using resources, which make a huge impact on a global level. The ideas like minimalism and simple living can help in further improving quality of life and stop exploitation of resources.
Growth always had been associated with ‘addition’ but in today’s time it is more about ‘subtraction’
As long as humans exist, they’ll continue to interfere with nature and disturb it’s natural cycle. In a way human existence itself is the most unsustainable thing for the planet. We’ll never want to cease existing, man as an animal will always fight and try to survive with changing conditions. All we can do is slow down the process of degradation of natural resources so we have enough time to correct our mistakes and keep evolving for the future. As the survival and extinction of man has directly been dependent on how man treated nature. What we see today as extinction could also actually be a stone age for the next chapter of human evolution.
List of References
- Limits to Growth – 30 year update, Donella Meadows, Jorgen Randers, Dennis Meadows, 2004.
- Lecture – Limits to growth. Dennis Meadows, ULM University, You Tube, 2019.
- Cosmos: A Spacetime Odyssey, Documentary, 2014.
- Thomas Malthus. Britannica, Website, 2012.
- Thomas Malthus, Wikipedia.
- Malthusian, Anti-Malthusian, Neo-Malthusian theory, Wikipedia.
Credits
Limits to Growth is an essay developed at Valldaura Labs of IaaC, Institute for Advanced Architecture of Catalonia from Master in Advanced Ecological Buildings and Biocities in (2021/2022) by:
Students: Kshitij Sarote, Prachi Agrawal
Faculty: Jordi Vivaldi