Problem
Robots are difficult to calibrate, it is a process that requires time and specific expertise to be achieved with precision. Plus, understanding kinematics and its applicability on different types of machines is a very complicated task. For this reason we decided to work around this problem teaching the machine to self-calibrate and determine its own kinematics.
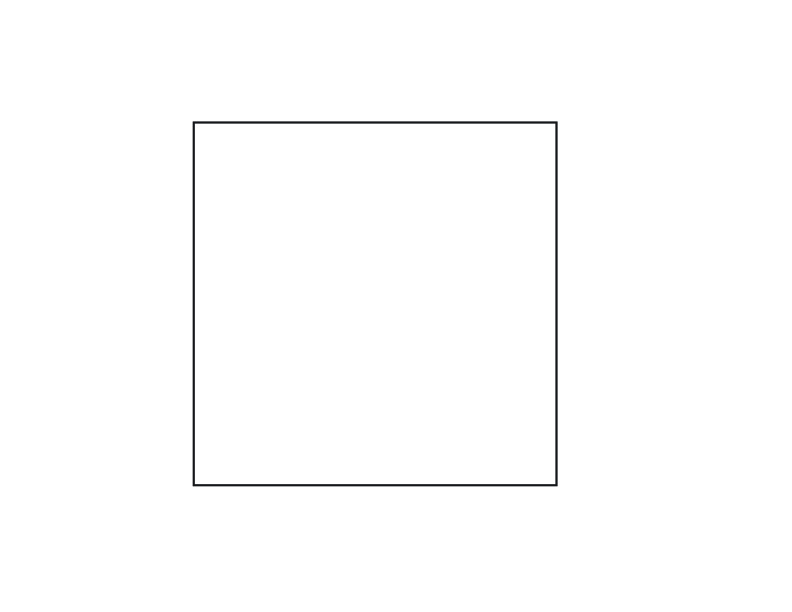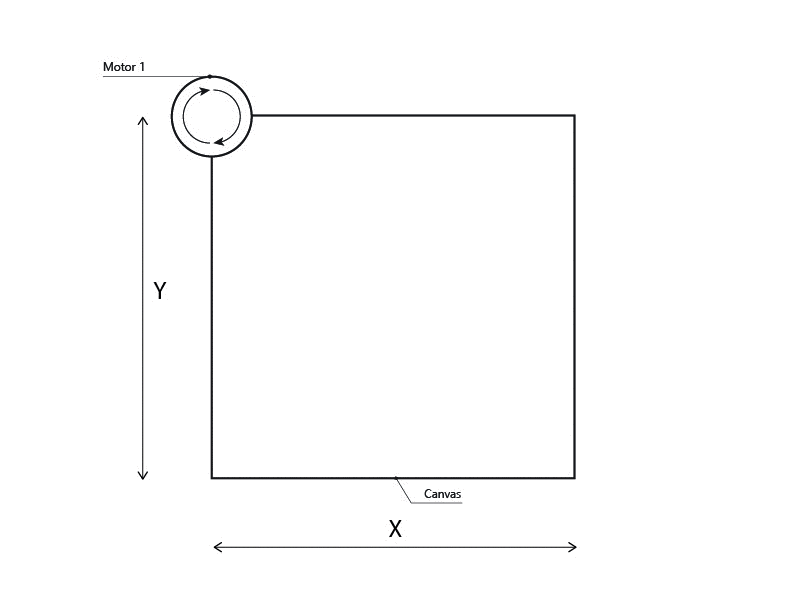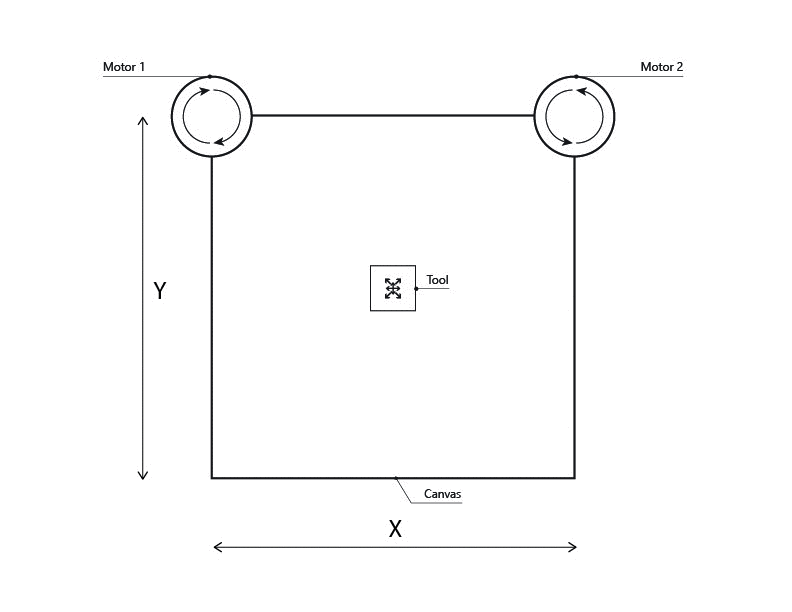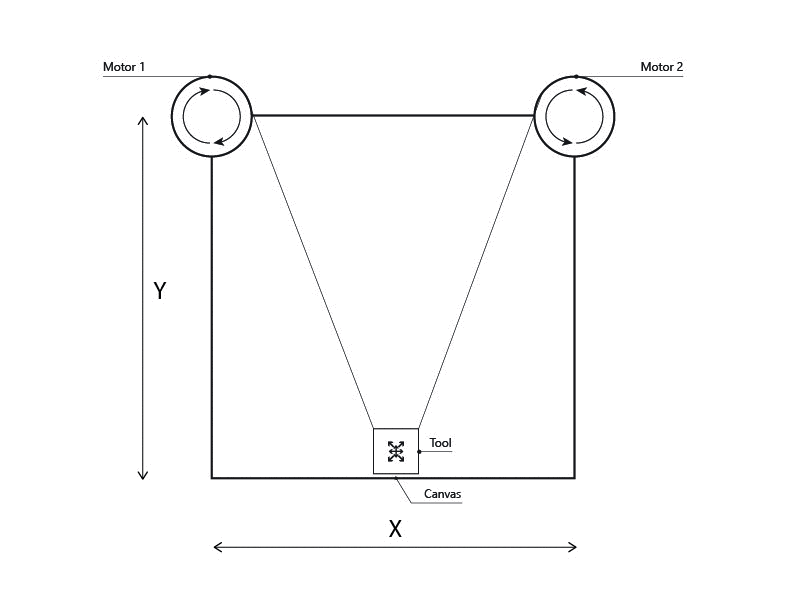
Q-Learning
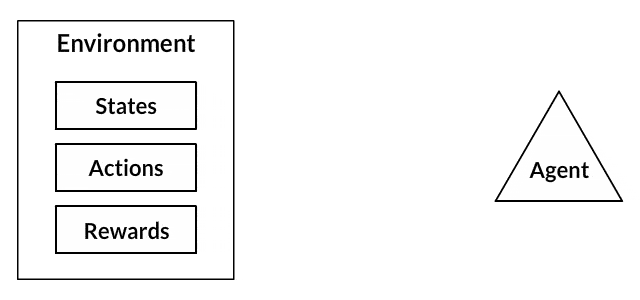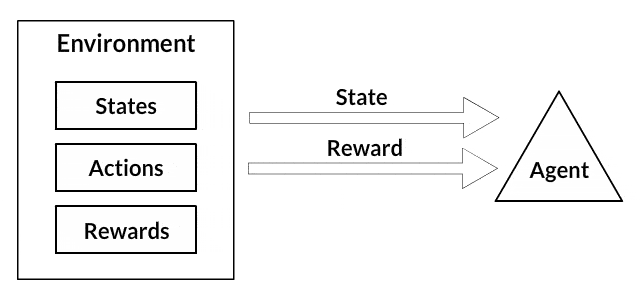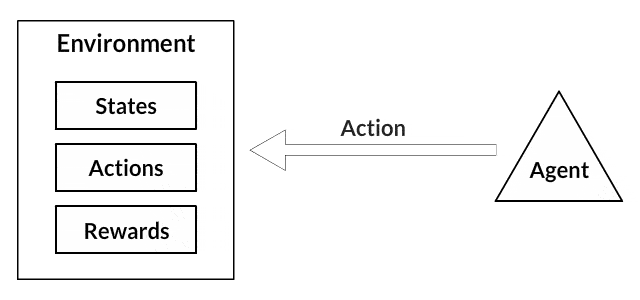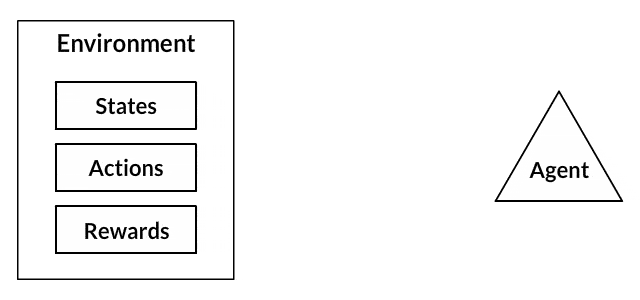
The process of Reinforcement Learning involves these simple steps:
- Observation of the environment.
- Deciding how to act using some strategy.
- Acting accordingly.
- Receiving a reward or penalty.
- Learning from the experiences and refining our strategy.
- Iterate until an optimal strategy is found.
Project Features
Setup
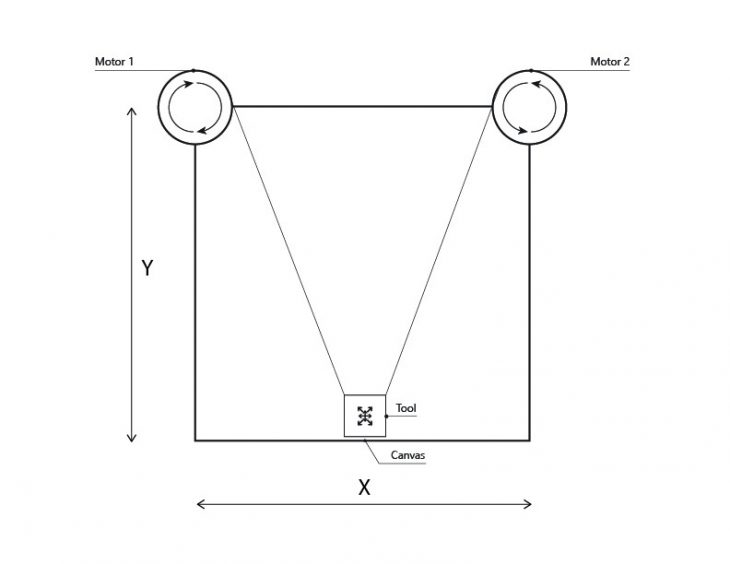
This project works as a vertical plotter, and its composed by:
- Two Nema17 stepper motors.
- 3D printed tool-head.
- External camera.
- Custom UI built in Python.
- 12V power source.
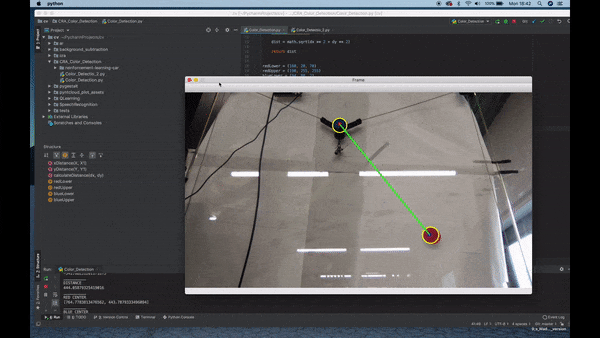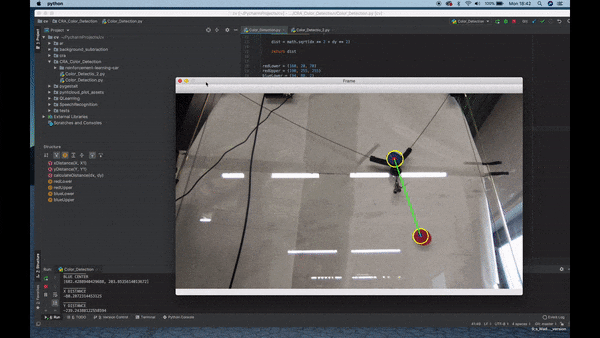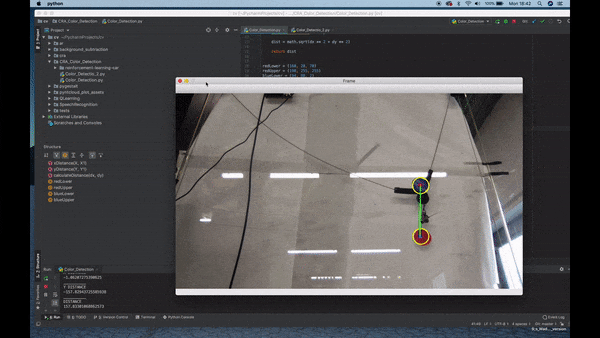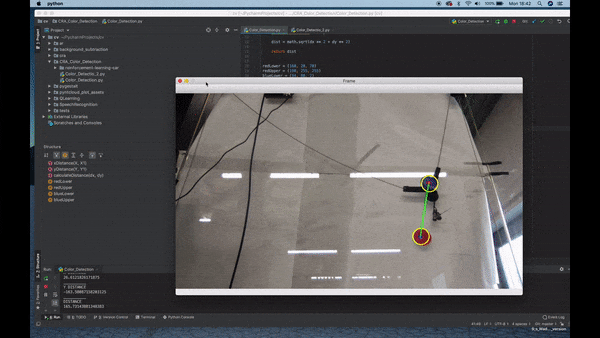
Color Detection
- Observation of the environment.
- Separate the image from the background.
- Detect color via (RGB /HSV /HSL).
- If the color has an Area bigger than a certain parameter sketch a circle around its shape.
- Once it finds the Area, detect the center of the geometry and draw a square.
- Connect the two centers with a line.
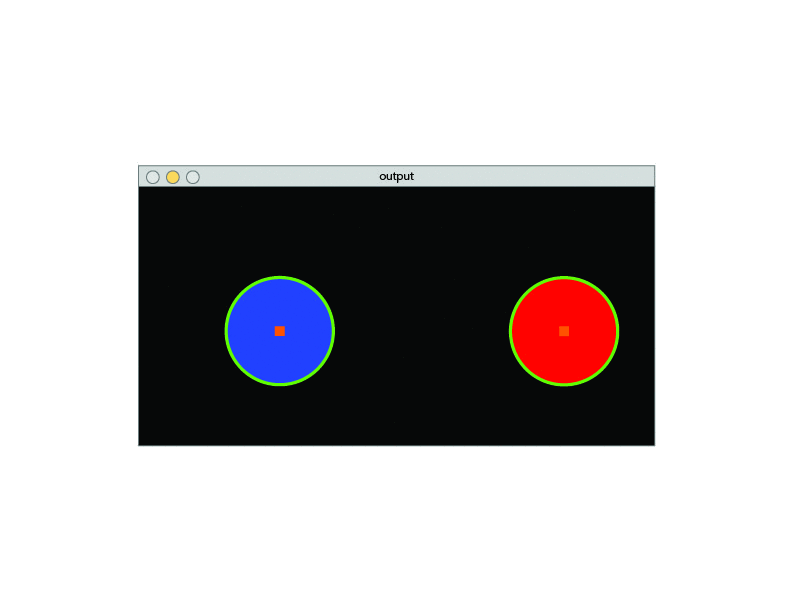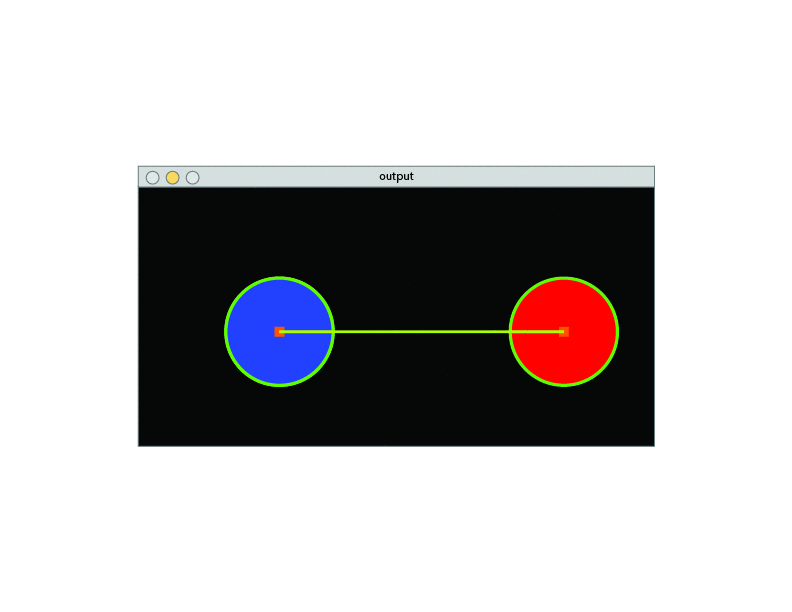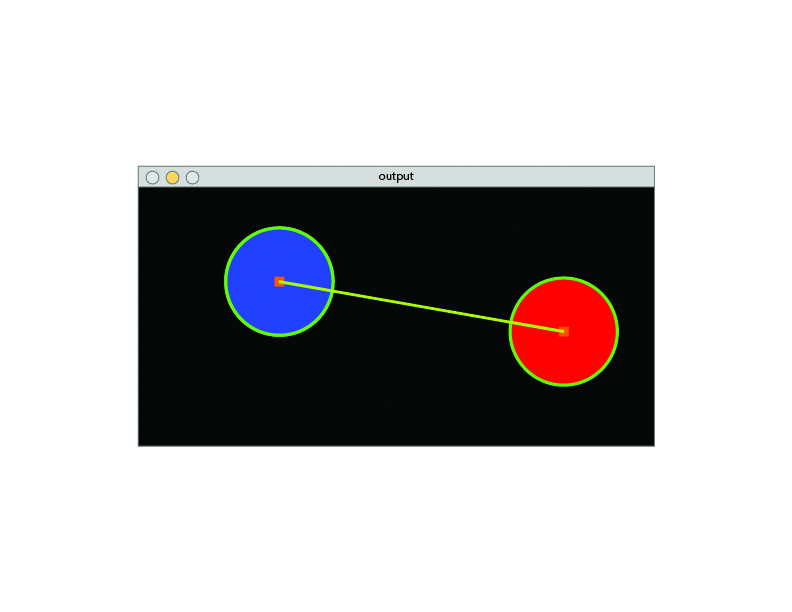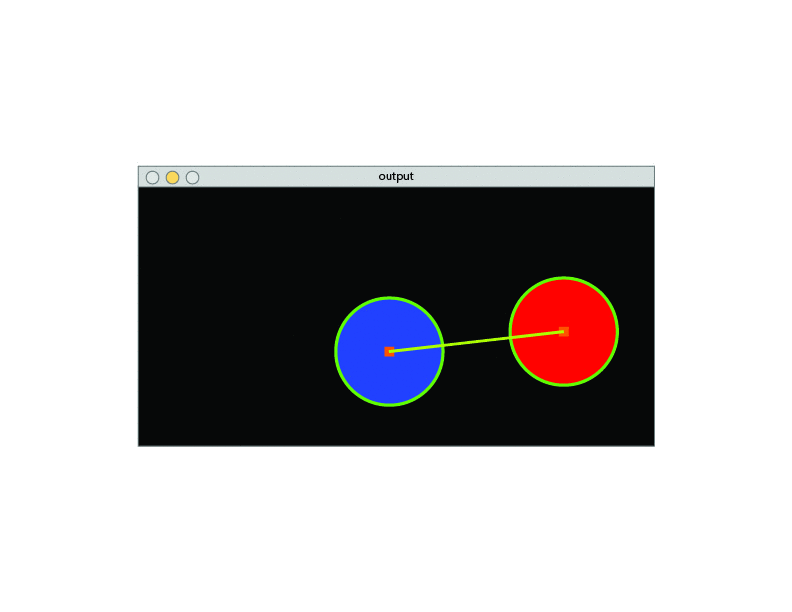
System Functioning
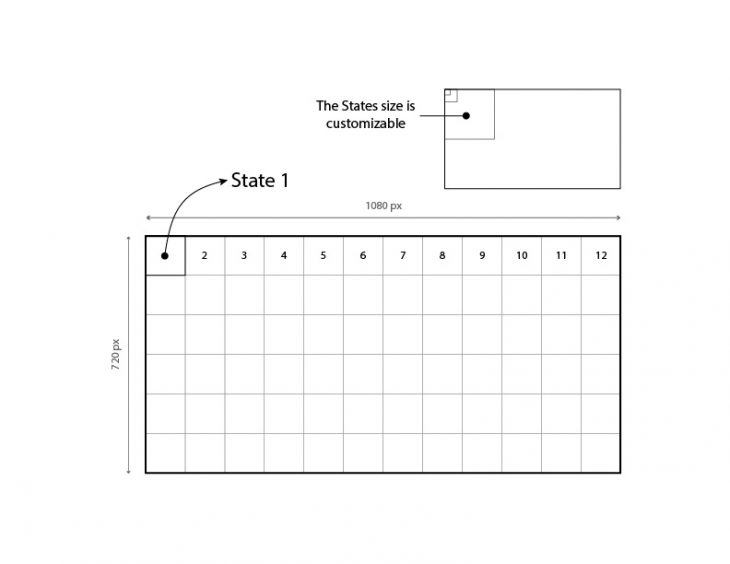
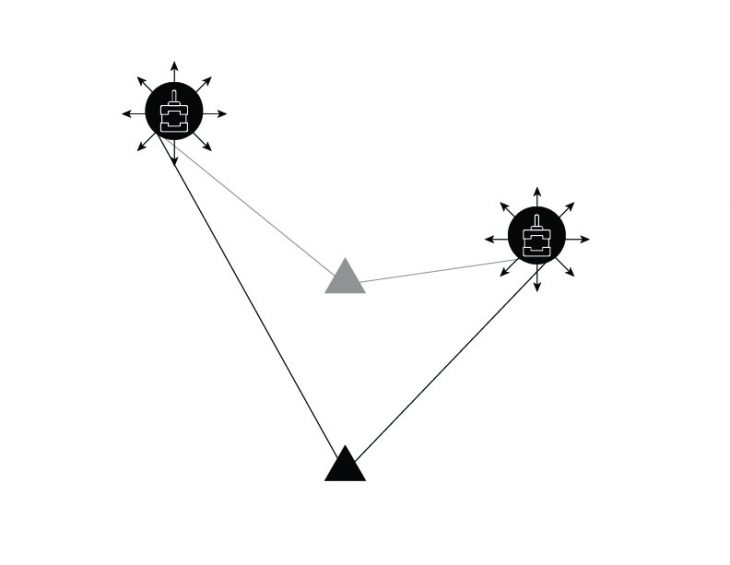
Subdivide the camera frame into sub-areas (States) in order to evaluate the distance “Agent-Target” based on the pixels feedback of the robot position.
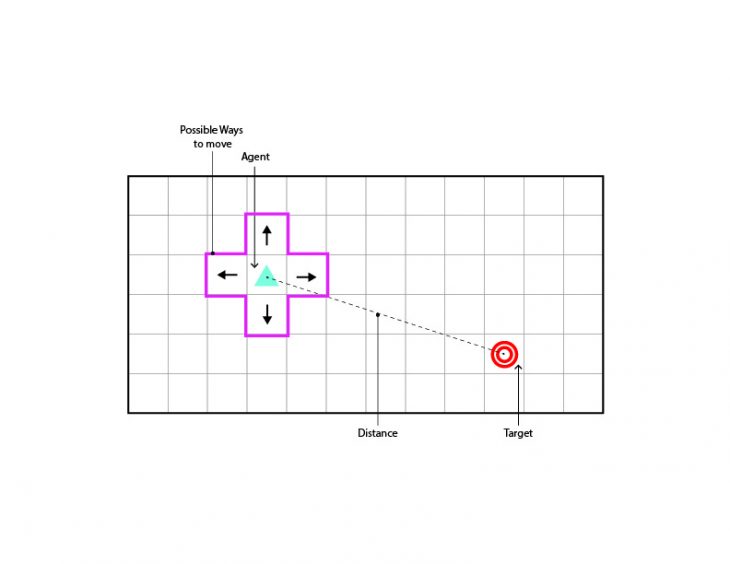
- Direction towards the target +
- Direction no towards the target –
- Robot hits boundary —
- Pick on target +
- Pick not on target –
- Place not on target –
- Place on target +
- Avoid obstacles
- Node 1 Clockwise
- Node 1 Counter-clockwise
- Node 2 Clockwise
- Node 2 Counter-clockwise
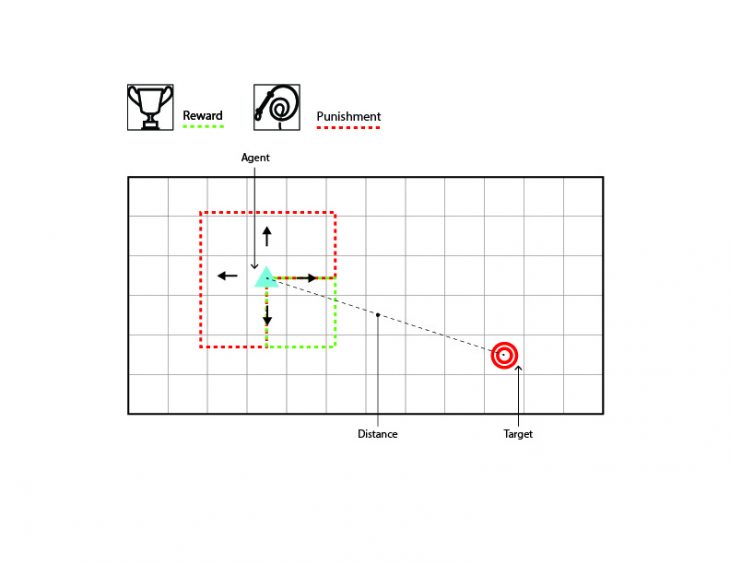
The robot gets a reward or a punishment about the right or wrong direction to the target.
- Agent (Tool)
- Target
The robot gets a reward or a punishment about the right or wrong position towards the target.
Advantages
The advantages of this technology are that the Motors can be placed in whatever way. Thanks to the self-configuring algorithm the tooltip will always locate itself in a space that will take it some iterations to understand where the boundaries are. Allowing a simpler use and more direct way to operate the robot.
Conclusions
The System works only as a proof of concept on our system (vertical-plotter), but we believe it could be applied to any type of robot, which would help to make it simpler and more accessible to a bigger range of workers and not only technicians.

Future Steps
- Achieving a more stable control over the computer vision color detection
- Extending the system from a 2D to a 3D environment
- Control an N number of motors at the same time without caring about the kinematics
Students: Riccardo Mura, Luis Arturo Pacheco Alcalà, Stefano Meloni
Faculty: Mateusz Zwierzycki
Tutor: Starsk Jose Lara