Responsive Bio-Climatic System for High-Density Residential Buildings in Sub-Tropical Climate is a Thesis project aimed at investigating the potential of incorporation of Bio-climatic systems in this case evaporation cooling mechanism in the design of High density housing projects.
Framework
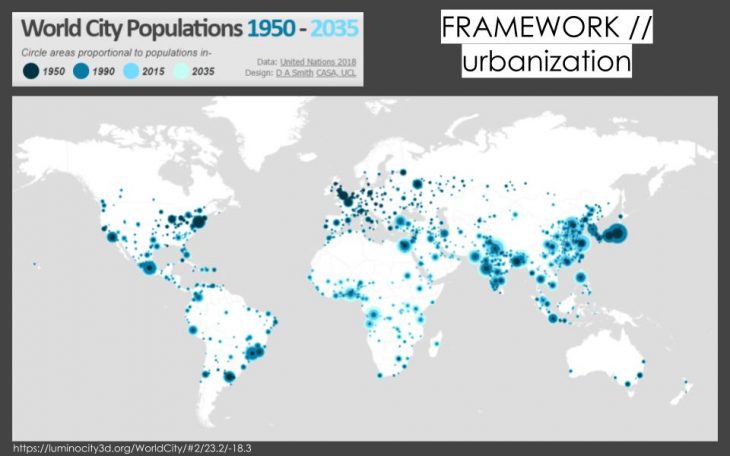
Urbanization
World Population is projected to reach unprecedented level and majority of the future population is projected to live in urban areas.
For the first time in history, more people live now in urban than in rural areas. In 2010, urban areas are home to 3.5 billion people, or 50.5 % of the world’s population. In the next four decades, all of the world’s population growth is expected to take place in urban areas, which will also draw in some of the rural population through rural to urban migration. Moreover, most of the expected urban growth will take place in developing countries, where the urban population is expected to double, from 2.6 billion in 2010 to 5.2 billion in 2050. In developed countries, the number of urban dwellers will grow more modestly, from 0.9 million in 2010 to 1.1 billion in 2050. During the same period, the world’s rural population will decline by 0.6 billion (1).
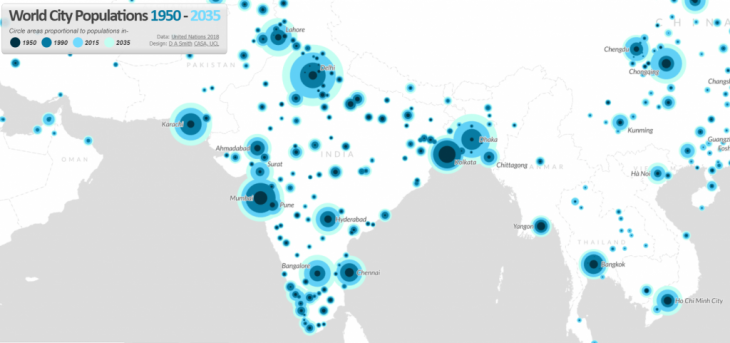
Indian cities are witnessing immense demographic expansion due to migration from surrounding villages, leading to urban sprawl, housing demand, rise in cost of land. Many citizens all over India migrate to the cities for better jobs and education. Industries, trade and commerce activities and number of educational cent res in cities attract floating population from all their surrounding villages and districts. This has expanded the cities in all directions and all aspects of development. With an urban sprawl of kilometers, these face the problems of congestion, pollution, everyday commuting to work place, competition, deforestation etc.
Climate Change
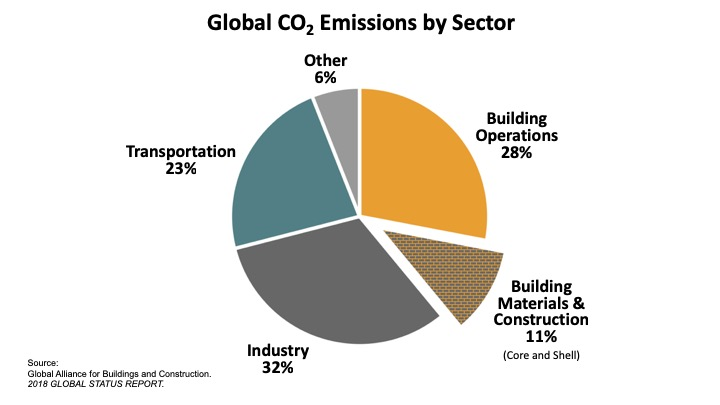 Carbon emissions have been increasing at an annual rate of 2% between 1971 and 2004 . This is particularly significant in the developing countries. One reason is the increasing demand in buildings due to the continuous growth of urban population. However, one of the growing trends in architecture to reduce the negative impacts of building construction and cope with the increase demand for new buildings is the high-rise buildings, in which developers increase the envelop height to satisfy the need for dense developments. This type of building could create a built environment that would be considered as sustainable, green, ecological, or bioclimatic. Thus, the ecological design of high-rise buildings is crucial and much more effective in those aspects than a green small building (2)
Carbon emissions have been increasing at an annual rate of 2% between 1971 and 2004 . This is particularly significant in the developing countries. One reason is the increasing demand in buildings due to the continuous growth of urban population. However, one of the growing trends in architecture to reduce the negative impacts of building construction and cope with the increase demand for new buildings is the high-rise buildings, in which developers increase the envelop height to satisfy the need for dense developments. This type of building could create a built environment that would be considered as sustainable, green, ecological, or bioclimatic. Thus, the ecological design of high-rise buildings is crucial and much more effective in those aspects than a green small building (2)
Annual magnitude of climate changes resulted from urbanization
| Parameter | Annual changes |
| Solar radiation | -22% |
| Air temperature | +1% |
| Relative humidity | -6% |
| Visibility (frequency) | -25% |
| Fog (frequency) | +60% |
| Wind speed | -25% |
| Cloudiness (frequency) | +8% |
| Rainfall (amount) | +14% |
| Thunderstorm (frequency) | +16% |
| Air pollution (volume) | +>1000% |
Urbanization can have a big impact on climate change.
As a main structure in a large city, the buildings and the services offered could have significant impacts in reducing the climate change effects if it is well managed starting from the plan and design stage. It must be considered in the context of mitigation, meaning, low running costs in carbon terms; that is related with energy consumption while comfort is maintained. [3]
Energy Use for Cooling
India is already the number-three spewer of greenhouse gases, burning through 800 million tonnes of coal every year — and the predicted AC boom could mean the country would have to triple its electricity production to meet demand, experts say.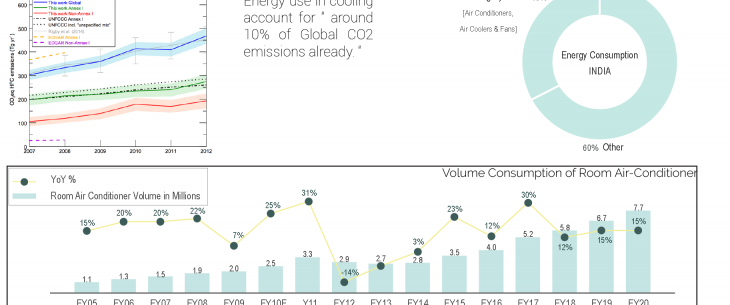
Oct 2020 // 2030 European Climate Target Plan The Commission’s proposal to cut greenhouse gas emissions by at least 55% by 2030 sets Europe on a responsible path to becoming climate neutral by 2050 .
2 Oct, 2019 // Energy demand for cooling accounts for nearly 10% of global electricity used around the world.
Cooling systems rely on human-made Hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs), which could account for nearly 20% of climate pollution by 2050, if not phased down and replaced with existing alternatives
8 Nov 2019 // India’s Climate Change Policy: Towards a Better Future The INDC has set a target of 175 GW of renewable energy by the year 2030 on the strength of the outstanding success of the National Solar Mission. It is reported that this capacity may well be achieved 10 years in advance. The government may raise India’s target to 227 GW for 2030. The target of achieving 40% of power from renewable sources by 2030 is likely to be achieved several years in advance.
16 May 2018 //Around 2.5 billion more people will be living in cities by 2050, projects new UN report
2018 //UNEP’s Sustainable Buildings and Construction Initiative (SBCI) are working to establish knowledge on the base-line emissions from buildings in India, highlight priority issues and opportunities for sustainable buildings and identify a network of experts that can contribute to the aims of Sustainable United Nations (SUN) and SBCI.
Thesis Statement
High-density residential buildings should incorporate Bio-climatic processes in their form for maintaining necessary thermal comfort level for the present and future urban inhabitants to break the perpetual cycle of relying on HVAC system to combat adverse effects of climate change including global warming .
Existing and widely used typology for high-rise residential buildings being SHELL AND CORE SYSTEM which due to its rigid structural composition and multiple shareholders makes the possibility of future interventions almost non-feasible, both structurally and financially.
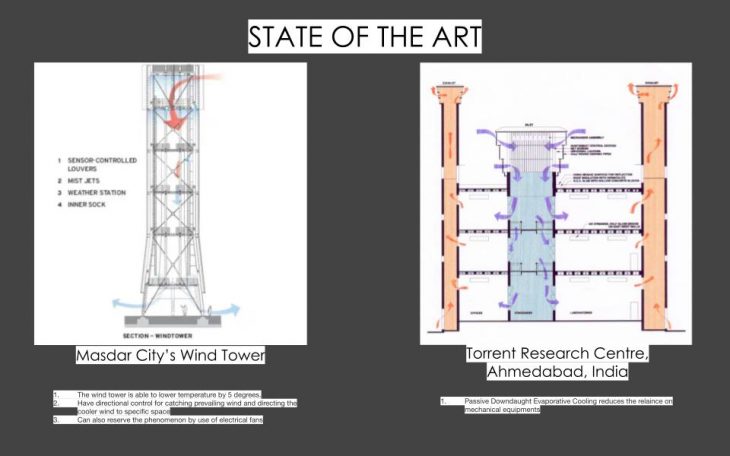
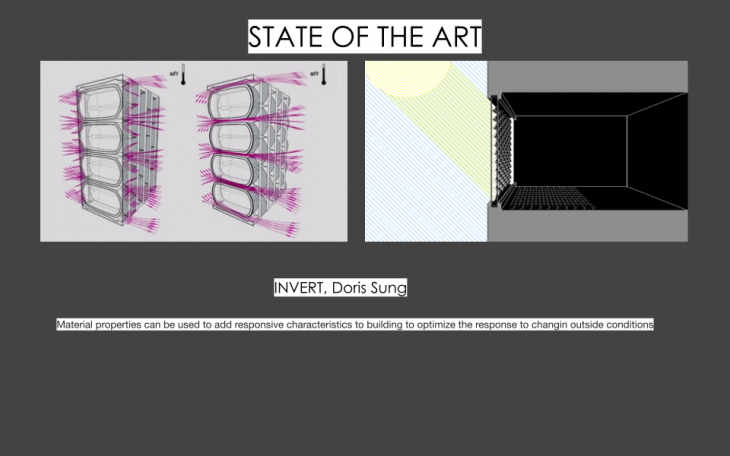
State of the Art
Site Parameters
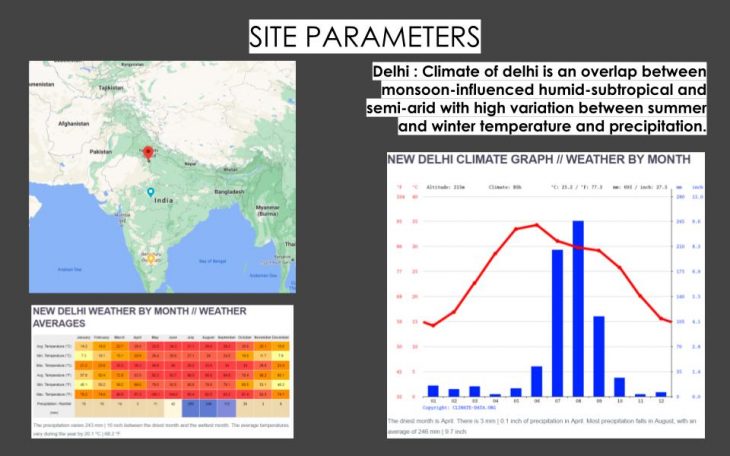
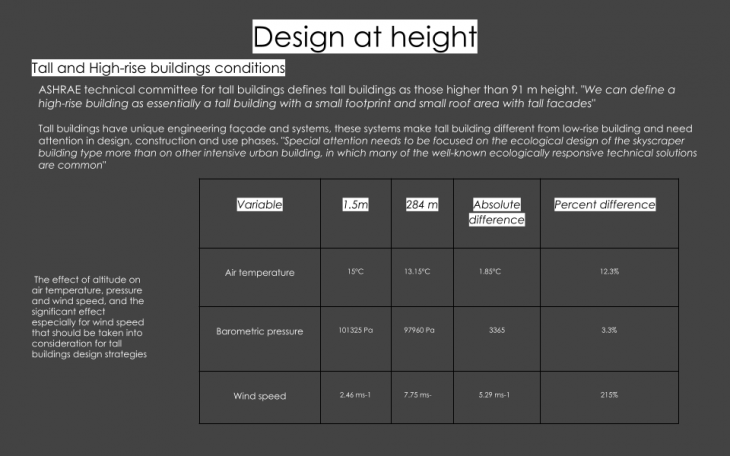
New Delhi is chosen as a location for the thesis investigation. Climatic data from New Delhi is used for design parameters.
Building Material
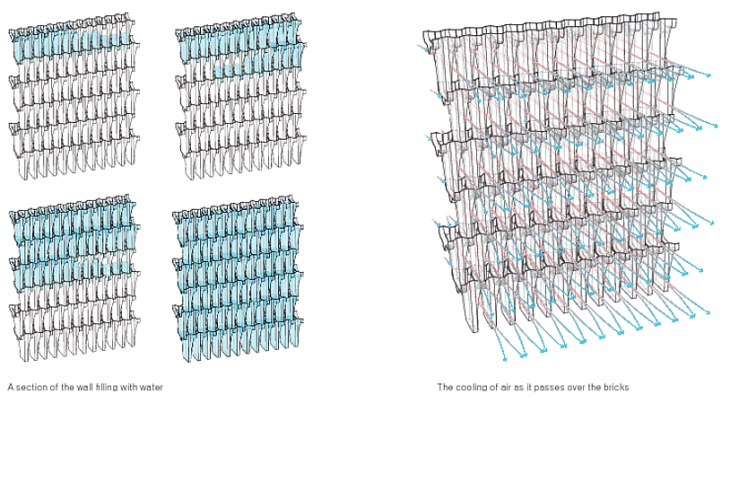
Terracotta
Terracotta is cheap to produce, durable, and has the unique ability to allow water to pass through its surface. This last quality makes terracotta an ideal material for designing evaporative cooling systems.
Terracotta pots have been historically being used in diverse regions of world for cooling period.
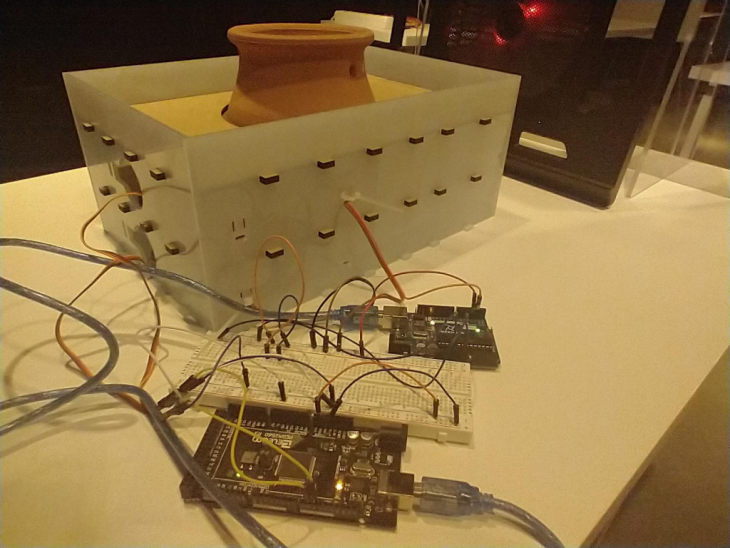
Experimental Setup
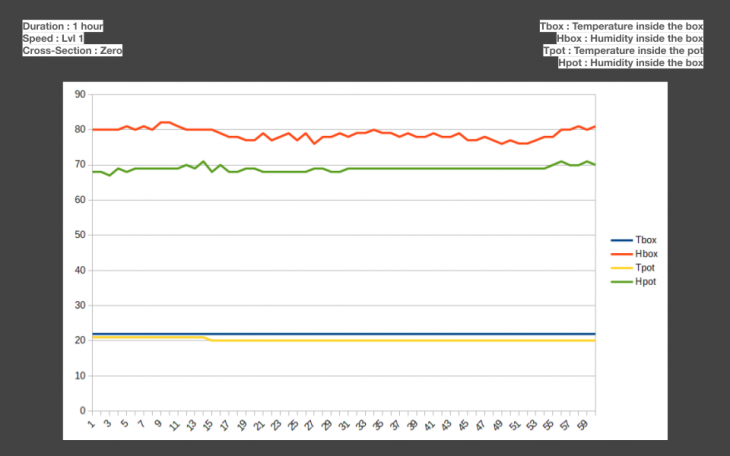
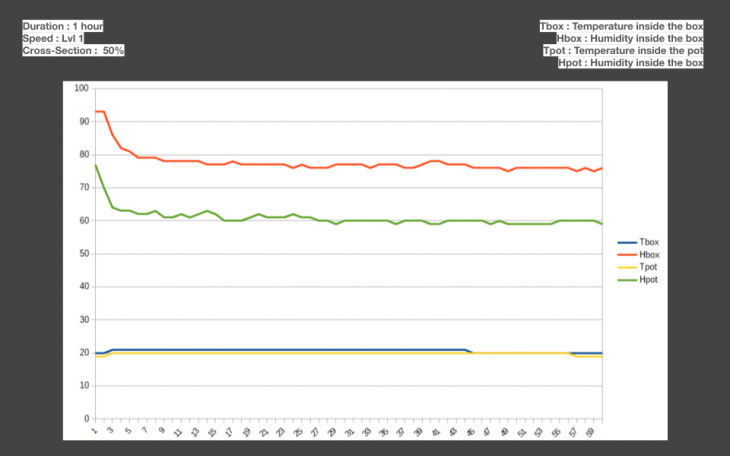
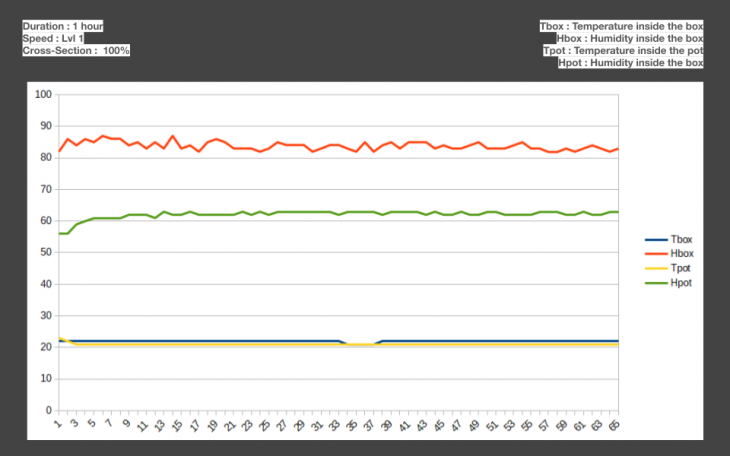
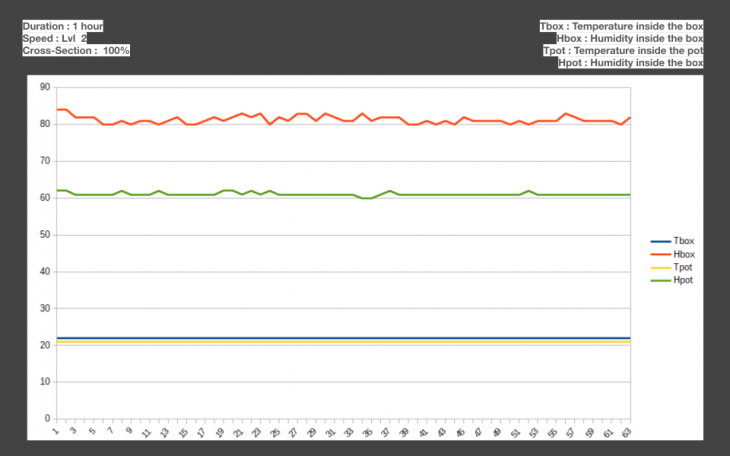
Duration : 1 hour
Temperature and Humidity Sensor
DHT_11
Scenarios to check hot air escape cross-section area
- Closed Lid
- Quarter Lid Open
- Half Lid Open
Fan Speed
- Normal
- 2X
 Duration : 1 hour
Duration : 1 hour
Temperature and Humidity
Fixed Water quantity
Surface Area : 686 cm2
Water Volume : 1 Litre
Conclusion of the data collection process
- Evaporative cooling with the current experimental setup needs longer duration to take effect.
- Duration of 1 hour was not sufficient
- During an earlier observation in duration of 3 hours, temperature of 2 degrees was observed inside the box.
- Temperature drop inside the box was observed.
- Inter-mediate cross-section resulted in to the desired 40-60% humidity level with normal wind speed.
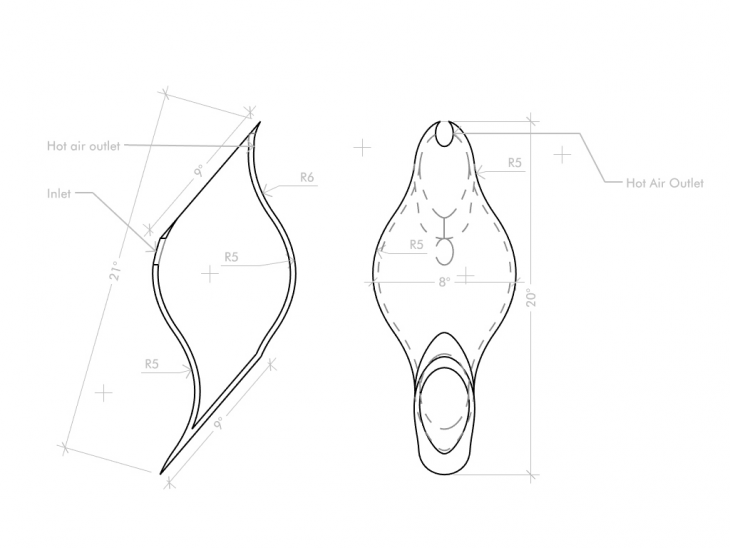
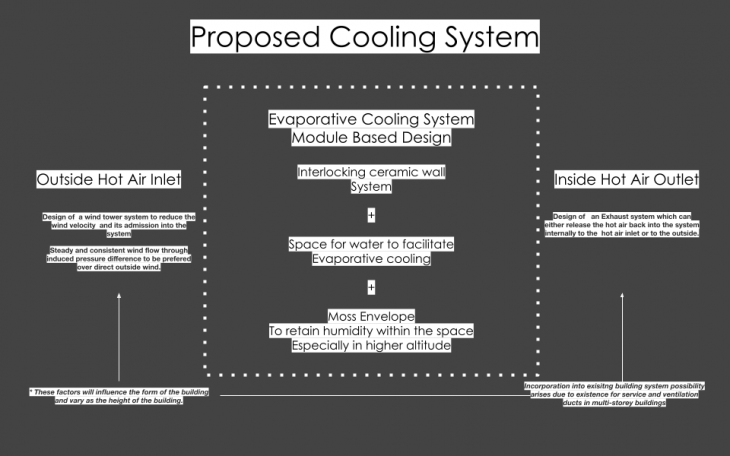
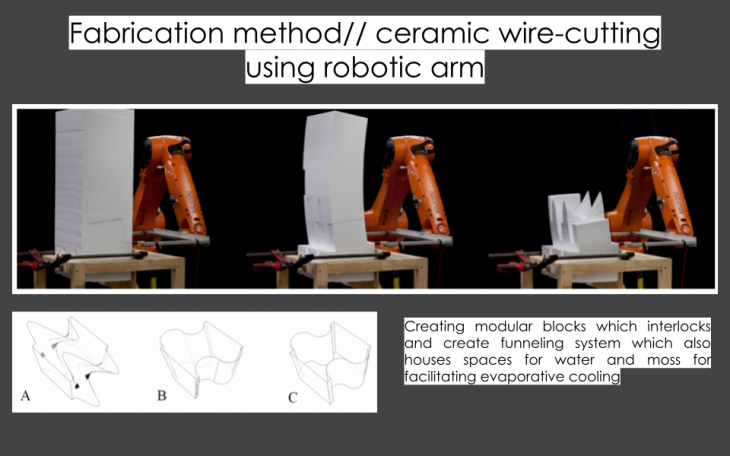
Module Design
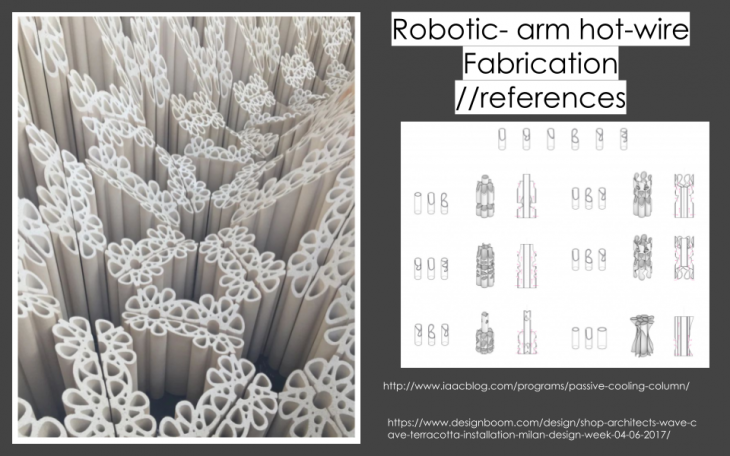
Evaporative Cooling References
Conclusion
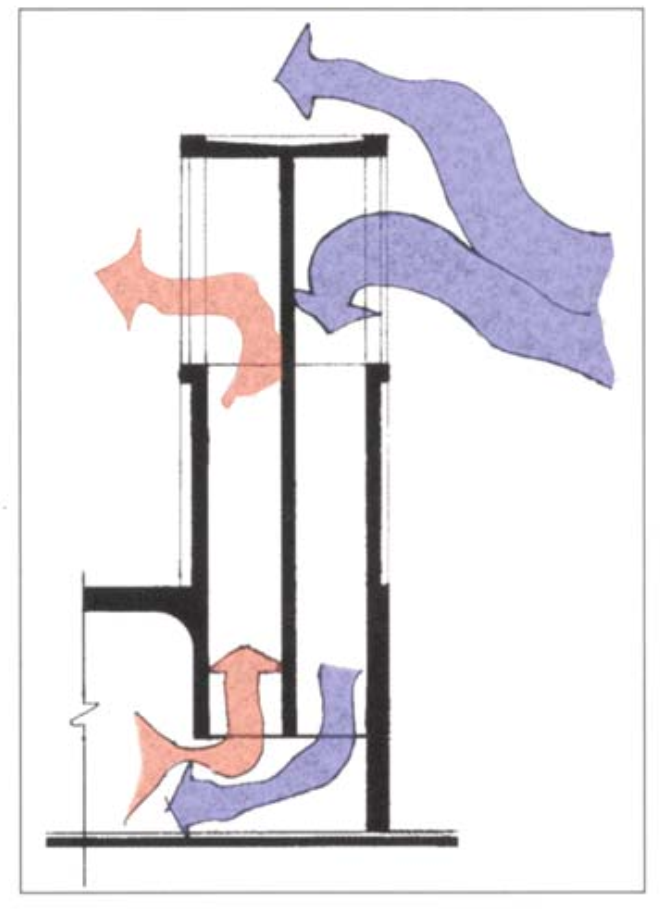
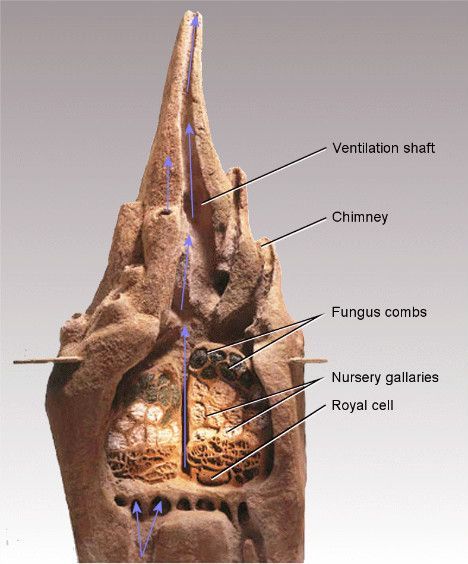
Termite Mound consists of Ventilation Shafts, Chimney, Fungus Combs, Nursery galleries and Royal cell among other places. Chimney and ventilation shafts constitute the majority of the volume of the termite mound and no living spaces. But it play the most essential role to maintain the desired temperature for fungus to grow and life to sustain within the Mound.
So the question is if in nature a dedicated space is designed to sustain life within a dwelling why don’t our buildings also design a space which does the same and reduce the adverse effect of our current design practices on the nature.
References
[1]
https://www.un.org/development/desa/en/news/population/2018-world-urbanization-prospects.html
[2]https://www.researchgate.net/publication/299695511_Cities_for_Smart_Environmental_and_Energy_Futures_Urban_Heat_Island_Mitigation_Techniques_for_Sustainable_Cities
[3] Sani, S. & Sham, A. M. (2007). Planning for an amenable biophysical climate in cities. IMPAK, 2, 8-9